Curcumin protects against bisphenol A-induced hepatic steatosis by inhibiting cholesterol absorption and synthesis in CD-1 mice
- PMID: 37701206
- PMCID: PMC10494624
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.3468
Curcumin protects against bisphenol A-induced hepatic steatosis by inhibiting cholesterol absorption and synthesis in CD-1 mice
Abstract
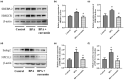
Curcumin is a polyphenol extracted from the rhizome of turmeric, and our previous research showed that curcumin inhibited cholesterol absorption and had cholesterol-lowering effect. Bisphenol A (BPA), a common plasticizer, is widely used in the manufacture of food packaging and is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). We hypothesized that curcumin could protect against BPA-induced hepatic steatosis by inhibiting cholesterol absorption and synthesis. Male CD-1 mice fed BPA-contaminated diet with or without curcumin for 24 weeks were used to test our hypothesis. We found that chronic low-dose BPA exposure significantly increased the levels of serum triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol (TC), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and the contents of liver TG and TC, resulting in liver fat accumulation and hepatic steatosis while curcumin supplementation could alleviate BPA-induced dyslipidemia and hepatic steatosis. Moreover, the anti-steatosis and cholesterol-lowering effects of curcumin against BPA coincided with a significant reduction in intestinal cholesterol absorption and liver cholesterol synthesis, which was modulated by suppressing the expression of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2 (SREBP-2), Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 (NPC1L1), and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase (HMGCR) in the small intestine and liver. In addition, the expression levels of liver lipogenic genes such as liver X receptor alpha (LXRα), SREBP-1c, acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 (ACC1), and ACC2 were also markedly down-regulated by curcumin. Overall, our findings indicated that curcumin inhibited BPA-induced intestinal cholesterol absorption and liver cholesterol synthesis by suppressing SREBP-2, NPC1L1, and HMGCR expression, subsequently reducing liver cholesterol accumulation and fat synthesis, thereby preventing hepatic steatosis and NAFLD.
Keywords: 3‐hydroxy‐3‐methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase; Niemann–Pick C1‐like 1; bisphenol A; curcumin; hepatic steatosis.
© 2023 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Curcumin protects against high-fat diet-induced nonalcoholic simple fatty liver by inhibiting intestinal and hepatic NPC1L1 expression via down-regulation of SREBP-2/HNF1α pathway in hamsters.J Nutr Biochem. 2023 Sep;119:109403. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2023.109403. Epub 2023 Jun 10. J Nutr Biochem. 2023. PMID: 37307885
-
Bisphenol A exposure induces cholesterol synthesis and hepatic steatosis in C57BL/6 mice by down-regulating the DNA methylation levels of SREBP-2.Food Chem Toxicol. 2019 Nov;133:110786. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2019.110786. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Food Chem Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31470036
-
Hepatoprotective effect of curcumin against bisphenol A-induced hepatic steatosis via modulating gut microbiota dysbiosis and related gut-liver axis activation in CD-1 mice.J Nutr Biochem. 2022 Nov;109:109103. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2022.109103. Epub 2022 Jun 30. J Nutr Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35780999
-
Hypocholesterolemic Activity of Curcumin Is Mediated by Down-regulating the Expression of Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 in Hamsters.J Agric Food Chem. 2017 Jan 18;65(2):276-280. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b04102. Epub 2017 Jan 3. J Agric Food Chem. 2017. PMID: 28000447
-
Protective Effects of Melatonin in High-Fat Diet-Induced Hepatic Steatosis via Decreased Intestinal Lipid Absorption and Hepatic Cholesterol Synthesis.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2023 Oct;38(5):557-567. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2023.1672. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2023. PMID: 37652870 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
StackNAFLD: An Accurate Stacking Ensemble Learning Targeting NAFLD Treatment.ACS Omega. 2025 Aug 15;10(33):37096-37114. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c01473. eCollection 2025 Aug 26. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40893275 Free PMC article.
-
Polyphenols Regulate the Activity of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals, Having Both Positive and Negative Effects.J Xenobiot. 2024 Oct 2;14(4):1378-1405. doi: 10.3390/jox14040077. J Xenobiot. 2024. PMID: 39449418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comprehensive review of medicinal plants and their beneficial roles in alleviating bisphenol A-induced organ toxicity.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul;398(7):7801-7876. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03795-8. Epub 2025 Feb 11. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39932506 Review.
-
Impacts of Curcumin Supplementation on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Patients With Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 2;8(3):e70525. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70525. eCollection 2025 Mar. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40041784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical Evidence of Curcuma longa Linn. as a Functional Food in the Management of Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Rodent Studies.Biomedicines. 2025 Aug 5;13(8):1911. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13081911. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40868165 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altmann, S. W. , Davis, H. R., Jr. , Zhu, L. J. , Yao, X. , Hoos, L. M. , Tetzloff, G. , Iyer, S. P. , Maguire, M. , Golovko, A. , Zeng, M. , Wang, L. , Murgolo, N. , & Graziano, M. P. (2004). Niemann‐pick C1 like 1 protein is critical for intestinal cholesterol absorption. Science, 303, 1201–1204. 10.1126/science.1093131 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cicero, A. F. G. , Sahebkar, A. , Fogacci, F. , Bove, M. , Giovannini, M. , & Borghi, C. (2020). Effects of phytosomal curcumin on anthropometric parameters, insulin resistance, cortisolemia and non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease indices: A double‐blind, placebo‐controlled clinical trial. European Journal of Nutrition, 59, 477–483. 10.1007/s00394-019-01916-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dallio, M. , Masarone, M. , Errico, S. , Gravina, A. G. , Nicolucci, C. , Di Sarno, R. , Gionti, L. , Tuccillo, C. , Persico, M. , Stiuso, P. , Diano, N. , Loguercio, C. , & Federico, A. (2018). Role of bisphenol a as environmental factor in the promotion of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease: in vitro and clinical study. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 47, 826–837. 10.1111/apt.14499 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Facina, C. H. , Campos, S. G. P. , Ruiz, T. F. R. , Góes, R. M. , Vilamaior, P. S. L. , & Taboga, S. R. (2021). Protective effect of the association of curcumin with piperine on prostatic lesions: New perspectives on BPA‐induced carcinogenesis. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 158, 112700. 10.1016/j.fct.2021.112700 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

