Literature review and guide for optimal position in implant-based breast reconstruction
- PMID: 37701292
- PMCID: PMC10493631
- DOI: 10.21037/gs-23-78
Literature review and guide for optimal position in implant-based breast reconstruction
Abstract
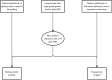
Background and objective: Identification of ideal candidates for prepectoral versus retropectoral implant-based breast reconstruction relies on careful preoperative risk assessment and intraoperative flap evaluation. Few guidelines exist to guide the surgeon's decision-making process when evaluating the preferred plane for implant placement.
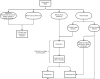
Methods: A literature review was performed to develop clinical decision-making algorithms for direct-to-implant (DTI) reconstruction with acellular dermal matrix (ADM) for patients undergoing prophylactic or therapeutic nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM) based on patient characteristics, surgical techniques, and outcomes.
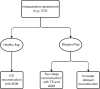
Key content and findings: Prepectoral reconstruction is most suitable for patients with small breasts or macromastia with desire for breast reduction, low-grade ptosis, smaller implant sizes, those undergoing PMRT, and for those who aim to mitigate animation deformity and capsular contracture. Retropectoral reconstruction may be recommended for patients with larger breasts with no desire for size change requiring additional prosthesis support, and in patients who aim to reduce likelihood of rippling and need for subsequent fat grafting procedures to address contour abnormalities.
Conclusions: Careful preoperative and intraoperative assessment of reconstruction options for patients undergoing implant-based breast reconstruction is necessary to mitigate complications and produce superior aesthetic outcomes. Decision algorithms may be used to determine ideal surgical techniques based on patient factors, like radiation history and planning, breast size and ptosis, and patient preferences.
Keywords: Implant-based breast reconstruction; decision algorithm; prepectoral; retropectoral.
2023 Gland Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://gs.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/gs-23-78/coif). CAS serves as an unpaid editorial board member of Gland Surgery from September 2022 to August 2024. EAT discloses a faculty position for Medtronic educational courses. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
