Incident pulmonary hypertension in 13 488 cases investigated with repeat echocardiography: a clinical cohort study
- PMID: 37701368
- PMCID: PMC10493707
- DOI: 10.1183/23120541.00082-2023
Incident pulmonary hypertension in 13 488 cases investigated with repeat echocardiography: a clinical cohort study
Abstract
Background: We addressed the paucity of data describing the characteristics and natural history of incident pulmonary hypertension.
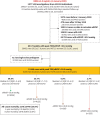
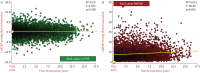
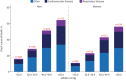
Methods: Adults (n=13 448) undergoing routine echocardiography without initial evidence of pulmonary hypertension (estimated right ventricular systolic pressure, eRVSP <30.0 mmHg) or left heart disease were studied. Incident pulmonary hypertension (eRVSP ≥30.0 mmHg) was detected on repeat echocardiogram a median of 4.1 years apart. Mortality was examined according to increasing eRVSP levels (30.0-39.9, 40.0-49.9 and ≥50.0 mmHg) indicative of mild-to-severe pulmonary hypertension.
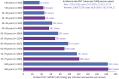
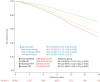
Results: A total of 6169 men (45.9%, aged 61.4±16.7 years) and 7279 women (60.8±16.9 years) without evidence of pulmonary hypertension were identified (first echocardiogram). Subsequently, 5412 (40.2%) developed evidence of pulmonary hypertension, comprising 4125 (30.7%), 928 (6.9%) and 359 (2.7%) cases with an eRVSP of 30.0-39.9 mmHg, 40.0-49.9 mmHg and ≥50.0 mmHg, respectively (incidence 94.0 and 90.9 cases per 1000 men and women, respectively, per year). Median (interquartile range) eRVSP increased by +0.0 (-2.27 to +2.67) mmHg and +30.68 (+26.03 to +37.31) mmHg among those with eRVSP <30.0 mmHg versus ≥50.0 mmHg. During a median 8.1 years of follow-up, 2776 (20.6%) died from all causes. Compared to those with eRVSP <30.0 mmHg, the adjusted risk of all-cause mortality was 1.30-fold higher in 30.0-39.9 mmHg, 1.82-fold higher in 40.0-49.9 mmHg and 2.11-fold higher in ≥50.0 mmHg groups (all p<0.001).
Conclusions: New-onset pulmonary hypertension, as indicated by elevated eRVSP, is a common finding among older patients without left heart disease followed-up with echocardiography. This phenomenon is associated with an increased morality risk even among those with mildly elevated eRVSP.
Copyright ©The authors 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: S. Stewart reports grants or contracts from NHMRC Australia, outside the submitted work; consulting fees from NEDA, outside the submitted work; and honoraria for presentations from Novartis Pharmaceuticals, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: D. Playford reports support for the present manuscript received from Johnson & Johnson. Conflict of interest: G.A. Strange reports support for the present manuscript received from Johnson & Johnson. Conflict of interest: The remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
