Nanoparticles and cytokine response
- PMID: 37701495
- PMCID: PMC10493271
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1243651
Nanoparticles and cytokine response
Abstract
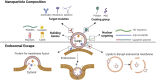
Synthetic nanoparticles (NPs) are non-viral equivalents of viral gene delivery systems that are actively explored to deliver a spectrum of nucleic acids for diverse range of therapies. The success of the nanoparticulate delivery systems, in the form of efficacy and safety, depends on various factors related to the physicochemical features of the NPs, as well as their ability to remain "stealth" in the host environment. The initial cytokine response upon exposure to nucleic acid bearing NPs is a critical component of the host response and, unless desired, should be minimized to prevent the unintended consequences of NP administration. In this review article, we will summarize the most recent literature on cytokine responses to nanoparticulate delivery systems and identify the main factors affecting this response. The NP features responsible for eliciting the cytokine response are articulated along with other factors related to the mode of therapeutic administration. For diseases arising from altered cytokine pathophysiology, attempts to silence the individual components of cytokine response are summarized in the context of different diseases, and the roles of NP features on this respect are presented. We finish with the authors' perspective on the possibility of engineering NP systems with controlled cytokine responses. This review is intended to sensitize the reader with important issues related to cytokine elicitation of non-viral NPs and the means of controlling them to design improved interventions in the clinical setting.
Keywords: biocompatibility; cytokine response; inflammatory response; nanoparticle; non-viral delivery.
Copyright © 2023 Nasrullah, Meenakshi Sundaram, Claerhout, Ha, Demirkaya and Uludag.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Azzam M., El Safy S., Abdelgelil S. A., Weiskirchen R., Asimakopoulou A., de Lorenzi F., et al. (2020). Targeting activated hepatic stellate cells using collagen-binding chitosan nanoparticles for siRNA delivery to fibrotic livers. Pharmaceutics 12 (6), 590. 10.3390/PHARMACEUTICS12060590 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

