N6-Methyladenosine-Modified ATP8B1-AS1 Exerts Oncogenic Roles in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Epigenetically Activating MYC
- PMID: 37701563
- PMCID: PMC10493143
- DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S415318
N6-Methyladenosine-Modified ATP8B1-AS1 Exerts Oncogenic Roles in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Epigenetically Activating MYC
Abstract
Purpose: N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification has shown critical roles in regulating mRNA fate. Non-coding RNAs also have important roles in various diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the potential influences of m6A modification on non-coding RNAs are still unclear. In this study, we identified a novel m6A-modified ATP8B1-AS1 and aimed to investigate the effects of m6A on the expression and role of ATP8B1-AS1 in HCC.
Methods: qPCR was performed to measure the expression of related genes. The correlation between gene expression and prognosis was analyzed using public database. m6A modification level was measured using MeRIP and single-base elongation- and ligation-based qPCR amplification method. The roles of ATP8B1-AS1 in HCC were investigated using in vitro and in vivo functional assays. The mechanisms underlying the roles of ATP8B1-AS1 were investigated by ChIRP and ChIP assays.
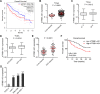
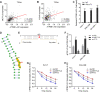
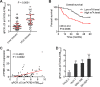
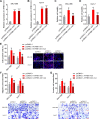
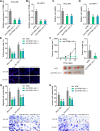
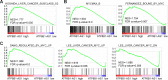
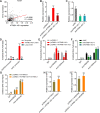
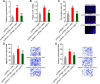
Results: ATP8B1-AS1 is highly expressed in HCC tissues and cell lines. High expression of ATP8B1-AS1 is correlated with poor overall survival of HCC patients. ATP8B1-AS1 is m6A modified and the 792 site of ATP8B1-AS1 is identified as an m6A modification site. m6A modification increases the stability of ATP8B1-AS1 transcript. m6A modification level of ATP8B1-AS1 is increased in HCC tissues and cell lines, and correlated with poor overall survival of HCC patients. ATP8B1-AS1 promotes HCC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, which were abolished by the mutation of m6A-modified 792 site. Mechanistic investigation revealed that m6A-modified ATP8B1-AS1 interacts with and recruits m6A reader YTHDC1 and histone demethylase KDM3B to MYC promoter region, leading to the reduction of H3K9me2 level at MYC promoter region and activation of MYC transcription. Functional rescue assays showed that depletion of MYC largely abolished the oncogenic roles of ATP8B1-AS1.
Conclusion: m6A modification level of ATP8B1-AS1 is increased and correlated with poor prognosis in HCC. m6A-modified ATP8B1-AS1 exerts oncogenic roles in HCC via epigenetically activating MYC expression.
Keywords: MYC signaling; N6-methyladenosine; hepatocellular carcinoma; histone methylation; noncoding RNA.
© 2023 Tan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
METTL3 and METTL14-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of SREBF2-AS1 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression and sorafenib resistance through DNA demethylation of SREBF2.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 14;14(1):6155. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55932-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38486042 Free PMC article.
-
m6A-Methylated NUTM2B-AS1 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Stemness Feature via Epigenetically Activating BMPR1A Transcription.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024 Dec 3;11:2393-2411. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S480522. eCollection 2024. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024. PMID: 39649245 Free PMC article.
-
N6-Methyladenosine-Modified LEAWBIH Drives Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression through Epigenetically Activating Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2023 Nov 6;10:1991-2007. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S433070. eCollection 2023. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2023. PMID: 37954496 Free PMC article.
-
N6 -methyladenosine-modified FAM111A-DT promotes hepatocellular carcinoma growth via epigenetically activating FAM111A.Cancer Sci. 2023 Sep;114(9):3649-3665. doi: 10.1111/cas.15886. Epub 2023 Jul 3. Cancer Sci. 2023. PMID: 37400994 Free PMC article.
-
Crispr-Cas9-based long non-coding RNA interference and activation identified that the aberrant expression of Myc-regulated ST8SIA6 antisense RNA 1 promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cytojournal. 2024 Nov 25;21:53. doi: 10.25259/Cytojournal_109_2024. eCollection 2024. Cytojournal. 2024. PMID: 39737136 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
METTL3 and METTL14-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of SREBF2-AS1 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression and sorafenib resistance through DNA demethylation of SREBF2.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 14;14(1):6155. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55932-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38486042 Free PMC article.
-
m6A-Methylated NUTM2B-AS1 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Stemness Feature via Epigenetically Activating BMPR1A Transcription.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024 Dec 3;11:2393-2411. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S480522. eCollection 2024. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024. PMID: 39649245 Free PMC article.
-
m6A-modified CTC-297N7.9 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis via epigenetically downregulating CCL2 and CD47.Cancer Cell Int. 2025 Jul 28;25(1):290. doi: 10.1186/s12935-025-03857-0. Cancer Cell Int. 2025. PMID: 40722171 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

