Adjuvant Lenvatinib Plus PD-1 Antibody for Hepatocellular Carcinoma with High Recurrence Risks After Hepatectomy: A Retrospective Landmark Analysis
- PMID: 37701564
- PMCID: PMC10493137
- DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S424616
Adjuvant Lenvatinib Plus PD-1 Antibody for Hepatocellular Carcinoma with High Recurrence Risks After Hepatectomy: A Retrospective Landmark Analysis
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of lenvatinib plus programmed death-1 (PD-1) antibody as postoperative adjuvant therapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) at high risks of recurrence.
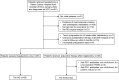
Patients and methods: A series of 137 patients with HCC at high risks of recurrence who underwent hepatectomy at our hospital between October 2019 and January 2022 were retrospectively analyzed. Recurrence-free survival (RFS), overall survival (OS), and treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) were assessed. Landmark analysis was used to compare short- and long-term RFS. Univariable and multivariable analyses were used to identify prognostic factors, and subgroup analyses were performed according to high risks of recurrence.
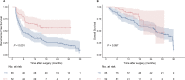
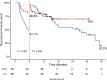
Results: A total of 85 patients underwent hepatectomy alone and 52 patients received postoperative adjuvant therapy. Compared with the hepatectomy group (HG), RFS was significantly improved in the adjuvant therapy group (ATG) (P < 0.001), but OS was not (P = 0.098). Landmark analysis revealed that RFS within 6 months of the HG was significantly different from that of the ATG (P < 0.001) but not after 6 months (P = 0.486). Multivariable analysis showed that without adjuvant therapy, high Child-Pugh classification, high alpha-fetoprotein levels, microvascular invasion, and satellite lesions were independent risk factors for recurrence within 6 months after hepatectomy. Subgroup analysis revealed that patients with MVI significantly benefited from adjuvant therapy in RFS. But for OS, adjuvant therapy was only significantly effective in patients with single tumor. The most common treatment-related adverse events during adjuvant therapy were hypertension (36.5%), rash or itching (28.8%), diarrhea (23.1%), and fatigue (21.2%).
Conclusion: Postoperative adjuvant lenvatinib plus PD-1 antibody significantly improved RFS in patients with HCC at high risks of recurrence with acceptable safeties.
Keywords: PD-1 antibody; efficacy; hepatocellular carcinoma; lenvatinib; postoperative adjuvant therapy; safety.
© 2023 Ouyang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflicts of interest to declare in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adjuvant anti-PD-1 antibody for hepatocellular carcinoma with high recurrence risks after hepatectomy.Hepatol Int. 2023 Apr;17(2):406-416. doi: 10.1007/s12072-022-10478-6. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Hepatol Int. 2023. PMID: 36645648
-
Survival Benefits From Adjuvant Lenvatinib for Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Microvascular Invasion After Curative Hepatectomy.Clin Med Insights Oncol. 2023 Jun 17;17:11795549231180351. doi: 10.1177/11795549231180351. eCollection 2023. Clin Med Insights Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37342206 Free PMC article.
-
Adjuvant camrelizumab plus apatinib in resected hepatocellular carcinoma with microvascular invasion: a multi-center real world study.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2024 Aug 1;13(4):616-631. doi: 10.21037/hbsn-23-363. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39175713 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of several postoperative adjuvant therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma patients with microvascular invasion after curative resection: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Feb 6;21(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01790-6. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 33549093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization improves survival outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma with microvascular invasion: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2019 Nov;45(11):2188-2196. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2019.06.031. Epub 2019 Jun 25. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31256949
Cited by
-
Roles of clinical application of lenvatinib and its resistance mechanism in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (Review).Am J Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 15;14(9):4113-4171. doi: 10.62347/UJVP4361. eCollection 2024. Am J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39417171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the efficacy of transarterial chemoembolization combined with microwave ablation followed by adjuvant therapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 6;15:1337396. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1337396. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38380330 Free PMC article.
-
Can adjuvant immune checkpoint inhibitors improve the long-term outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma with high-risk recurrent factors after liver resection? A meta-analysis and systematic review.Front Oncol. 2024 May 24;14:1374262. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1374262. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38854716 Free PMC article.
-
Adjuvant HAIC combined with anlotinib and TQB2450 for resected high-risk hepatocellular carcinoma.Innovation (Camb). 2025 Apr 11;6(7):100910. doi: 10.1016/j.xinn.2025.100910. eCollection 2025 Jul 7. Innovation (Camb). 2025. PMID: 40697792 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

