BIOLOGICAL ANTIARRHYTHMICS-SODIUM CHANNEL INTERACTING PROTEINS
- PMID: 37701589
- PMCID: PMC10493736
BIOLOGICAL ANTIARRHYTHMICS-SODIUM CHANNEL INTERACTING PROTEINS
Abstract
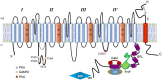
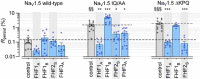
Voltage gated Na channels (NaV) are essential for excitation of tissues. Mutations in NaVs cause a spectrum of human disease from autism and epilepsy to cardiac arrhythmias to skeletal myotonias. The carboxyl termini (CT) of NaV channels are hotspots for disease-causing mutations and are richly invested with protein interaction sites. We have focused on the regulation of NaV by two proteins that bind in this region: calmodulin (CaM) and non-secreted fibroblast growth factors (iFGF or FHF). CaM regulates NaV gating, mediating Ca2+-dependent inactivation (CDI) in a channel isoform-specific manner, while Ca2+-free CaM (apo-CaM) binding broadly regulates NaV opening and suppresses the arrhythmogenic late Na current (INa-L). FHFs inhibit CDI, in NaV isoforms that exhibit this property, and potently suppress INa-L, the latter requiring the amino terminus of the FHF. A peptide comprised of the first 39 amino acids of FHF1A is sufficient to inhibit INa-L, constituting a credible specific antiarrhythmic.
© 2023 The American Clinical and Climatological Association.
Figures





References
-
- Chugh SS, Jui J, Gunson K, et al. Current burden of sudden cardiac death: multiple source surveillance versus retrospective death certificate-based review in a large U.S. community. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44(6):1268–75. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2004.06.029. - PubMed
-
- Fouda MA, Ghovanloo MR, Ruben PC. Late sodium current: incomplete inactivation triggers seizures, myotonias, arrhythmias, and pain syndromes. J Physiol. 2022;600(12):2835–51. doi:10.1113/JP282768. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
