Multi-target action of Garcinia livingstonei extract and secondary metabolites against fatty acid synthase, α-glucosidase, and xanthine oxidase
- PMID: 37701752
- PMCID: PMC10494472
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2023.101762
Multi-target action of Garcinia livingstonei extract and secondary metabolites against fatty acid synthase, α-glucosidase, and xanthine oxidase
Abstract
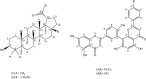
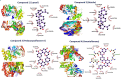
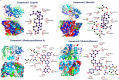
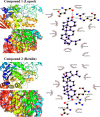
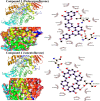
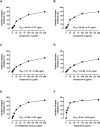
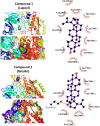
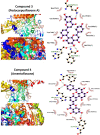
Garcinia livingstonei is a traditional herbal medicine that showed beneficial health effects and bioactivities. Four compounds have been isolated from the plant leaves and were elucidated as lupeol, betulin, podocarpusflavone A, and amentoflavone. The inhibitory activities of G. livingstonei extract and isolated metabolites against fatty acid synthase (FAS), α-glucosidase, and xanthine oxidase (XO) were investigated in vitro. The affinity of the compounds toward the studied enzymes was investigated in silico. The plant extract inhibited FAS, α-glucosidase, and XO with IC50 values of 26.34, 67.88, and 33.05 µg/mL, respectively. Among the isolated metabolites, betulin exhibited the most inhibitory activity against α-glucosidase and XO with IC50 values of 38.96 and 30.94 µg/mL, respectively. Podocarpusflavone A and betulin were the most potent inhibitors of FAS with IC50 values of 24.08 and 27.96 µg/mL, respectively. Computational studies corroborated these results highlighting the interactions between metabolites and the enzymes. In conclusion, G. livingstonei and its constituents possess the potential to modulate enzymes involved in metabolism and oxidative stress.
Keywords: Alpha-glucosidase; Fatty acid synthase; Garcinia livingstonei; Xanthine oxidase.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Antioxidant, Anti-Diabetic, and Anti-Inflammation Activity of Garcinia livingstonei Aqueous Leaf Extract: A Preliminary Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 10;25(6):3184. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063184. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542158 Free PMC article.
-
Xanthine oxidase inhibition study of isolated secondary metabolites from Dolichandrone spathacea (Bignoniaceae): In vitro and in silico approach.Saudi Pharm J. 2024 Apr;32(4):101980. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2024.101980. Epub 2024 Feb 5. Saudi Pharm J. 2024. PMID: 38439949 Free PMC article.
-
Non-toxic melanin production inhibitors from Garcinia livingstonei (Clusiaceae).J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Sep 16;149(2):570-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.07.023. Epub 2013 Jul 23. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23891889
-
Bioactive compounds from Carissa opaca roots and xanthine oxidase and alpha-amylase inhibitory activities of their methanolic extract and its fractions in different solvents.Pharmacognosy Res. 2014 Oct-Dec;7(4):295-301. doi: 10.4103/0974-8490.158440. Pharmacognosy Res. 2014. PMID: 26692741 Free PMC article.
-
Lipophilic extracts of Leucas zeylanica, a multi-purpose medicinal plant in the tropics, inhibit key enzymes involved in inflammation and gout.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Oct 5;224:474-481. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.04.042. Epub 2018 May 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29727733
Cited by
-
Antioxidant, Anti-Diabetic, and Anti-Inflammation Activity of Garcinia livingstonei Aqueous Leaf Extract: A Preliminary Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 10;25(6):3184. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063184. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542158 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdullahi S., Musa A., Abdullahi M., et al. Isolation of Lupeol from the Stem-bark of Lonchocarpus sericeus (Papilionaceae) Scholars Acad. J. Biosci. 2013;1:18–19.
-
- Abukhalil M.H., Hussein O.E., Bin-Jumah M., et al. Farnesol attenuates oxidative stress and liver injury and modulates fatty acid synthase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase in high cholesterol-fed rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020;27:30118–30132. - PubMed
-
- Acuna U.M., Dastmalchi K., Basile M.J., et al. Quantitative high-performance liquid chromatography photo-diode array (HPLC-PDA) analysis of benzophenones and biflavonoids in eight Garcinia species. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2012;25:215–220.
-
- Antar S.A., Abdo W., Taha R.S., et al. Telmisartan attenuates diabetic nephropathy by mitigating oxidative stress and inflammation, and upregulating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling in diabetic rats. Life Sci. 2022;291 - PubMed
-
- Baggett S., Protiva P., Mazzola E.P., et al. Bioactive benzophenones from Garcinia xanthochymus fruits. J. Nat. Prod. 2005;68:354–360. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

