Elucidating individual differences in chronic pain and whole person health with allostatic load biomarkers
- PMID: 37701788
- PMCID: PMC10493889
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbih.2023.100682
Elucidating individual differences in chronic pain and whole person health with allostatic load biomarkers
Abstract
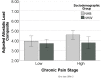
Chronic pain is a stressor that affects whole person functioning. Persistent and prolonged activation of the body's stress systems without adequate recovery can result in measurable physiological and neurobiological dysregulation recognized as allostatic load. We and others have shown chronic pain is associated with measures of allostatic load including clinical biomarker composites, telomere length, and brain structures. Less is known regarding how different measures of allostatic load align. The purpose of the study was to evaluate relationships among two measures of allostatic load: a clinical composite and pain-related brain structures, pain, function, and socioenvironmental measures. Participants were non-Hispanic black and non-Hispanic white community-dwelling adults between 45 and 85 years old with knee pain. Data were from a brain MRI, questionnaires specific to pain, physical and psychosocial function, and a blood draw. Individuals with all measures for the clinical composite were included in the analysis (n = 175). Indicating higher allostatic load, higher levels of the clinical composite were associated with thinner insula cortices with trends for thinner inferior temporal lobes and dorsolateral prefrontal cortices (DLPFC). Higher allostatic load as measured by the clinical composite was associated with greater knee osteoarthritis pathology, pain disability, and lower physical function. Lower allostatic load as indicated by thicker insula cortices was associated with higher income and education, and greater physical functioning. Thicker insula and DLPFC were associated with a lower chronic pain stage. Multiple linear regression models with pain and socioenvironmental measures as the predictors were significant for the clinical composite, insular, and inferior temporal lobes. We replicate our previously reported bilateral temporal lobe group difference pattern and show that individuals with high chronic pain stage and greater socioenvironmental risk have a higher allostatic load as measured by the clinical composite compared to those individuals with high chronic pain stage and greater socioenvironmental buffers. Although brain structure differences are shown in individuals with chronic pain, brain MRIs are not yet clinically applicable. Our findings suggest that a clinical composite measure of allostatic load may help identify individuals with chronic pain who have biological vulnerabilities which increase the risk for poor health outcomes.
Keywords: Allostatic load; Brain structure; Chronic pain; Knee pain; Socioenvironmental factors; Stress.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article which may be considered as potential competing interests:
Figures
References
-
- Apkarian A.V., Bushnell M.C., Treede R.-D., Zubieta J.-K. Human brain mechanisms of pain perception and regulation in health and disease. Eur. J. Pain. 2005;9(4) 463-463. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources