Depression and anxiety in acute ischemic stroke involving the anterior but not paramedian or inferolateral thalamus
- PMID: 37701875
- PMCID: PMC10493383
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1218526
Depression and anxiety in acute ischemic stroke involving the anterior but not paramedian or inferolateral thalamus
Abstract
Background and objectives: Emotional and cognitive deficits are prevalent in strokes involving the thalamus. In contrast to cognitive deficits, emotional deficits have not been studied prospectively in isolated thalamic stroke.
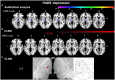
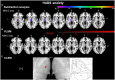
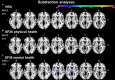
Methods: In 37 ischemic thalamic stroke patients (57.0 [50.0; 69.5] years [median (Q1; Q3)], 21 males, 5 anterior, 12 paramedian, 20 inferolateral vascular territory), and 37 non-stroke control patients matched for age and sex, we prospectively examined depression, anxiety, activities of daily living, and quality of life at 1, 6, 12, and 24 months post-stroke using the Hospital-Anxiety-and-Depression Scale (HADS), Nürnberger-Alters-Alltagsaktivitäten scale (NAA), and Short Form-36 (SF36) questionnaire. Voxel-based lesion-symptom mapping (VLSM) and lesion-subtraction analyzes were performed to determine associations between questionnaire scores and thalamic stroke topography.
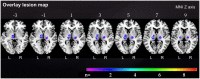
Results: At 1 month post-stroke, anterior thalamic stroke patients had higher depression scores [8.0 (7.5; 10.5)] than paramedian [4.5 (1.0; 5.8)] and inferolateral [4.0 (1.0; 7.0)] thalamic stroke patients. Furthermore, anterior thalamic stroke patients had higher anxiety scores [11.0 (8.0; 14.5)] than their matched controls [2.5 (2.0; 2.5)], paramedian [4.5 (1.0; 5.8)] and inferior [4.0 (1.0; 7.0)] thalamic stroke patients. Depression and anxiety scores in anterior thalamic stroke patients remained high across the follow-up [depression: 9.0 (3.5; 13,8); anxiety:10.05 (2.8, 14.5)].Physical health assessed by SF36 was intact in anterior [1 month post-stroke: T-score = 55.9 (37.0; 57.6)] but reduced in inferolateral [44.5(32.4; 53.1)] thalamic stroke, whereas mental health was reduced in anterior thalamic stroke [32.0 (29.8; 47.3)].VLSM confirmed that voxels in the anterior thalamus around Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) coordinates X = -8, Y = -12, Z = 2 were more often affected by the stroke in depressed (HADS-score ≥ 8) than non-depressed (HADS-score < 8) patients and voxels around coordinates X = -10, Y = -12, Z = 2 were more often affected in anxious (HADS-score ≥ 8) than non-anxious (HADS-score < 8) patients.
Conclusion: Anterior, but not paramedian or inferolateral thalamic stroke was associated with depression and anxiety. Even though our results are mostly significant in the left thalamus, this observation on stroke laterality might be confounded by the fact that the right hemisphere was underrepresented in our study.
Keywords: anxiety; brain infarct; depression; emotion; magnetic resonance imaging; voxel-based lesion-symptom mapping.
Copyright © 2023 Scharf, Gronewold, Eilers, Todica, Moenninghoff, Doeppner, de Haan, Bassetti and Hermann.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evolution of Neuropsychological Deficits in First-Ever Isolated Ischemic Thalamic Stroke and Their Association With Stroke Topography: A Case-Control Study.Stroke. 2022 Jun;53(6):1904-1914. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.037750. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Stroke. 2022. PMID: 35259928 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency and phenotype of thalamic aphasia.J Neurol. 2022 Jan;269(1):368-376. doi: 10.1007/s00415-021-10640-4. Epub 2021 Jun 8. J Neurol. 2022. PMID: 34100990 Free PMC article.
-
Social cognitive and neurocognitive deficits in inpatients with unilateral thalamic lesions - pilot study.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015 Apr 10;11:1031-8. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S78037. eCollection 2015. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015. PMID: 25914535 Free PMC article.
-
Inferolateral thalamic ischemia secondary to PCA P2 perforator occlusion mimics MCA stroke syndrome.Neurosurg Rev. 2020 Feb;43(1):339-342. doi: 10.1007/s10143-019-01211-3. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Neurosurg Rev. 2020. PMID: 31709467 Review.
-
Clinical and Neuroimaging Findings in Thalamic Territory Infarctions: A Review.J Neuroimaging. 2018 Jul;28(4):343-349. doi: 10.1111/jon.12503. Epub 2018 Feb 20. J Neuroimaging. 2018. PMID: 29460331 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of obstructive sleep apnea, neurofilaments and early CPAP intervention in post-stroke cognitive recovery.Sleep Med X. 2025 May 31;10:100142. doi: 10.1016/j.sleepx.2025.100142. eCollection 2025 Dec 15. Sleep Med X. 2025. PMID: 40546265 Free PMC article.
-
Differential impact of cerebral small vessel disease on thalamic regulation of anxiety: insights from 7T MRI.Mol Psychiatry. 2025 Sep;30(9):4142-4150. doi: 10.1038/s41380-025-02994-2. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Mol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40169803
-
Subcortical Alterations in Newly Diagnosed Epilepsy and Associated Changes in Brain Connectivity and Cognition.Hum Brain Mapp. 2024 Nov;45(16):e70069. doi: 10.1002/hbm.70069. Hum Brain Mapp. 2024. PMID: 39508641 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aben I., Verhey F., Lousberg R., Lodder J., Honig A. (2002). Validity of the Beck depression inventory, hospital anxiety and depression scale, Scl-90, and Hamilton depression rating scale as screening instruments for depression in stroke patients. Psychosomatics 43, 386–393. doi: 10.1176/appi.psy.43.5.386, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alizadeh Z., Roohafza H., Feizi A., Sarrafzadegan N. (2021). Association of Cigarette Smoking with depression and anxiety in middle-aged adults: a large cross-sectional study among Iranian industrial manufacturing employees. Int. J. Ment. Heal. Addict. 21, 1700–1712. doi: 10.1007/s11469-021-00684-y - DOI
-
- Aragona B., De Luca R., Piccolo A., Le Cause M., Destro M., Casella C., et al. . (2018). Is bupropion useful in the treatment of post-stroke thalamic apathy? A case report and considerations. Funct. Neurol. 33, 213–216. PMID: - PubMed

