Exploiting endovascular aortic repair as a minimally invasive method - Nine years of experience in a non-university hospital
- PMID: 37701925
- PMCID: PMC10493885
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejro.2023.100522
Exploiting endovascular aortic repair as a minimally invasive method - Nine years of experience in a non-university hospital
Abstract
Background: At the introduction of endovascular aortic repair (EVAR) in 2013 in our non-university hospital, we established a quality registry to monitor our EVAR activity.
Purpose: To observe if we over time were able to exploit EVAR as a minimally invasive method in an elective as well as emergency setting, and to monitor our treatment quality in terms of complications, secondary interventions and mortality.
Material and methods: From November 2013 to March 2022, we treated 207 patients with EVAR, including six patients with rupture. Follow-up regimen was partly based on contrast-enhanced computer tomography, and partly on contrast-enhanced ultrasound in combination with plain radiography.
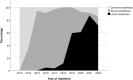
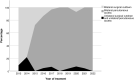
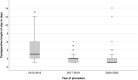
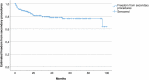
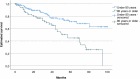
Results: During the observation period, the method of anesthesia changed from general, via spinal, to local anesthesia. The groin access changed from surgical cut down to percutaneous and the median length of postoperative stay decreased from 3 days to 1 day. EVAR on ruptured aneurysm was done for the first time in 2019. Endoleak was detected in 85 patients (42%) and 37 patients (18%) had one or more secondary interventions, of which 85% were endovascular. Estimated five-year survival was 72% in patients below 80 years of age and 45% in patients 80 years or older.
Conclusion: Nine years of experience enabled us to exploit EVAR's advantages as a minimally invasive method in an elective as well as emergency setting. Complications, secondary interventions and survival rates in our low volume non-university hospital matches results from larger vascular centers.
Keywords: Aneurysm; Aorta; Interventional; Vascular.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2002;2(1):1-46. Epub 2002 Mar 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2002. PMID: 23074438 Free PMC article.
-
Fenestrated endovascular grafts for the repair of juxtarenal aortic aneurysms: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009;9(4):1-51. Epub 2009 Jul 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009. PMID: 23074534 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of midterm results of endovascular aneurysm repair for ruptured and elective abdominal aortic aneurysms.J Vasc Surg. 2020 May;71(5):1554-1563.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2019.07.091. Epub 2019 Oct 31. J Vasc Surg. 2020. PMID: 31677942
-
Clinical presentation, operative management, and long-term outcomes of rupture after previous abdominal aortic aneurysm repair.J Vasc Surg. 2023 Feb;77(2):396-405.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2022.08.005. Epub 2022 Oct 19. J Vasc Surg. 2023. PMID: 36272507 Review.
-
Five-year outcomes of physician-modified endografts for repair of complex abdominal and thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms.J Vasc Surg. 2023 Feb;77(2):374-385.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2022.09.019. Epub 2022 Nov 8. J Vasc Surg. 2023. PMID: 36356675 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic Radial MR Imaging for Endoleak Surveillance after Endovascular Repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms with Inconclusive CT Angiography: A Prospective Study.J Clin Med. 2024 May 15;13(10):2913. doi: 10.3390/jcm13102913. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38792455 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krajcer Z., Ramaiah V.G., Henao E.A., Metzger D.C., Nelson W.K., Moursi M.M., Rajasinghe H.A., Al-Dallow R., Miller L.E. Perioperative outcomes from the prospective multicenter least invasive fast-track EVAR (LIFE) registry. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2018;25(1):6–13. - PubMed
-
- Robinson W.P. Open versus endovascular repair of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms: what have we learned after more than 2 decades of ruptured endovascular aneurysm repair? Surgery. 2017;162(6):1207–1218. - PubMed
-
- Antoniou G.A., Antoniou S.A., Torella F. Editor's choice - endovascular vs. open repair for abdominal aortic aneurysm: systematic review and meta-analysis of updated peri-operative and long term data of randomised controlled trials. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2020:385–397. - PubMed
-
- Varabyova Y., Blankart C.R., Schreyögg J. The role of learning in health technology assessments: an empirical assessment of endovascular aneurysm repairs in german hospitals. Health Econ. 2017;26(Suppl 1):93–108. - PubMed
-
- Jones M., Koury H., Faris P., Moore R. Impact of an emergency endovascular aneurysm repair protocol on 30-day ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm mortality. J. Vasc. Surg. 2022;76(3):663–670. e2. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources