Polycomb safeguards imaginal disc specification through control of the Vestigial-Scalloped complex
- PMID: 37702007
- PMCID: PMC10560572
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.201872
Polycomb safeguards imaginal disc specification through control of the Vestigial-Scalloped complex
Abstract
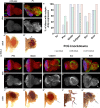
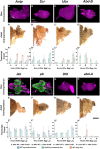
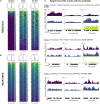
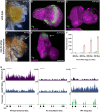
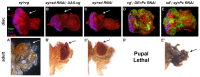
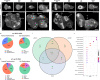
A fundamental goal of developmental biology is to understand how cell and tissue fates are specified. The imaginal discs of Drosophila are excellent model systems for addressing this paradigm as their fate can be redirected when discs regenerate after injury or when key selector genes are misregulated. Here, we show that when Polycomb expression is reduced, the wing selector gene vestigial is ectopically activated. This leads to the inappropriate formation of the Vestigial-Scalloped complex, which forces the eye to transform into a wing. We further demonstrate that disrupting this complex does not simply block wing formation or restore eye development. Instead, immunohistochemistry and high-throughput genomic analysis show that the eye-antennal disc unexpectedly undergoes hyperplastic growth with multiple domains being organized into other imaginal discs and tissues. These findings provide insight into the complex developmental landscape that tissues must navigate before adopting their final fate.
Keywords: Drosophila; Epigenetics; Eye; Imaginal disc; Polycomb; Scalloped; Vestigial; Wing.
© 2023. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

Update of
-
Polycomb safeguards imaginal disc specification through control of the Vestigial-Scalloped complex.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 12:2023.04.11.536444. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.11.536444. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Development. 2023 Sep 15;150(18):dev201872. doi: 10.1242/dev.201872. PMID: 37090526 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Al Hajri, Q., Dash, S., Feng, W.-C., Garner, H. R. and Anandakrishnan, R. (2020). Identifying multi-hit carcinogenic gene combinations: Scaling up a weighted set cover algorithm using compressed binary matrix representation on a GPU. Sci. Rep. 10, 2022. 10.1038/s41598-020-58785-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

