Brain-derived neurotrophic factor genetic polymorphism rs6265 and creativity
- PMID: 37703265
- PMCID: PMC10499242
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291397
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor genetic polymorphism rs6265 and creativity
Abstract
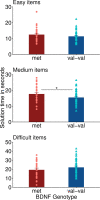
The protein brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) promotes neural plasticity of the central nervous system and plays an important role for learning and memory. A single nucleotide polymorphism (rs6265) at position 66 in the pro-region of the human BDNF gene, resulting in a substitution of the amino acid valine (val) with methionine (met), leads to attenuated BDNF secretion and has been associated with reduced neurocognitive function. Inhomogeneous results have been found regarding the effect of the BDNF genotype on behavior. We determined the BDNF genotype and performance on the Compound Remote Associate (CRA) task as a common measure of creativity in 76 healthy university students. In our main analyses, we did not find significant differences between met-carriers (n = 30) and non-met carriers (n = 46). In a secondary analysis, we found that met-carriers had a slower solution time (medium effect size) for items of medium difficulty. Our results suggest that met-carriers and non-met-carriers do not generally differ regarding their creativity, but non-met-carriers may have a certain advantage when it comes to moderately difficult problems. The wider literature suggests that both genetic variants come with advantages and disadvantages. Future research needs to sharpen our understanding of the disadvantages and, potentially, advantages met allele carriers may have.
Copyright: © 2023 Hertenstein et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report there are no competing interests to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A protective effect of the BDNF Met/Met genotype in obesity in healthy Caucasian subjects but not in patients with coronary heart disease.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016 Aug;20(16):3417-26. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27608901
-
Generation of three induced pluripotent stem cell lines carrying different variants of the BDNF (Val66Met) polymorphism.Stem Cell Res. 2023 Feb;66:102989. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2022.102989. Epub 2022 Dec 5. Stem Cell Res. 2023. PMID: 36473250
-
Impact of brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism on cortical thickness and voxel-based morphometry in healthy Chinese young adults.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e37777. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037777. Epub 2012 Jun 13. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22719849 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene polymorphisms on motor performance and motor learning: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Behav Brain Res. 2022 Feb 26;420:113712. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113712. Epub 2021 Dec 13. Behav Brain Res. 2022. PMID: 34915075
-
The association of the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and the hippocampal volumes in healthy humans: a joint meta-analysis of published and new data.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2014 May;42:267-78. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.03.011. Epub 2014 Mar 24. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2014. PMID: 24674929 Review.
Cited by
-
The influence of serotonergic multilocus genetic variants and parent-child relationship on adolescent creativity.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21013. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-03038-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595767 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous