Chiral recognition of neutral guests by chiral naphthotubes with a bis-thiourea endo-functionalized cavity
- PMID: 37704639
- PMCID: PMC10499783
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-41390-8
Chiral recognition of neutral guests by chiral naphthotubes with a bis-thiourea endo-functionalized cavity
Abstract
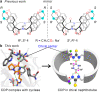
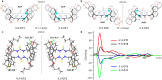
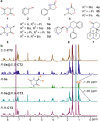
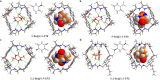
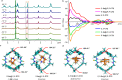
Developing chiral receptors with an endo-functionalized cavity for chiral recognition is of great significance in the field of molecular recognition. This study presents two pairs of chiral naphthotubes containing a bis-thiourea endo-functionalized cavity. Each chiral naphthotube has two homochiral centers which were fixed adjacent to the thiourea groups, causing the skeleton and thiourea groups to twist enantiomerically through chiral transfer. These chiral naphthotubes are highly effective at enantiomerically recognizing various neutral chiral molecules with an enantioselectivity up to 17.0. Furthermore, the mechanism of the chiral recognition has been revealed to be originated from differences in multiple non-covalent interactions. Various factors, such as the shape of cavities, substituents of guests, flexibility of host and binding modes are demonstrated to contribute to creating differences in the non-covalent interactions. Additionally, the driving force behind enantioselectivity is mainly attributed to enthalpic differences, and enthalpy -entropy compensation has also been observed to influence enantioselectivity.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enantioselective Recognition of Functional Organic Molecules in Water by Biomimetic Macrocyclic Hosts.J Am Chem Soc. 2024 Feb 14;146(6):3900-3909. doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c11492. Epub 2024 Jan 31. J Am Chem Soc. 2024. PMID: 38294833
-
Naphthotubes: Macrocyclic Hosts with a Biomimetic Cavity Feature.Acc Chem Res. 2020 Jan 21;53(1):198-208. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00415. Epub 2019 Dec 20. Acc Chem Res. 2020. PMID: 31858790 Review.
-
Aryl-Extended and Super Aryl-Extended Calix[4]pyrroles: Design, Synthesis, and Applications.Acc Chem Res. 2023 Feb 21;56(4):500-513. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.2c00839. Epub 2023 Feb 2. Acc Chem Res. 2023. PMID: 36734050
-
Dynamic Control of Chiral Recognition in Water-Soluble Naphthotubes Induced by Hydrostatic Pressure.ACS Nanosci Au. 2024 Oct 21;4(6):435-442. doi: 10.1021/acsnanoscienceau.4c00052. eCollection 2024 Dec 18. ACS Nanosci Au. 2024. PMID: 39713726 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in chiral recognition using macrocyclic receptors.Chem Commun (Camb). 2025 May 20;61(42):7573-7584. doi: 10.1039/d5cc00828j. Chem Commun (Camb). 2025. PMID: 40298286 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigating the diastereoselective synthesis of a macrocycle under Curtin-Hammett control.Chem Sci. 2024 Mar 5;15(15):5516-5524. doi: 10.1039/d3sc05715a. eCollection 2024 Apr 17. Chem Sci. 2024. PMID: 38638241 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular recognition and potentiometric determination of neostigmine and pyridostigmine by a methylene-bridged naphthotube.RSC Adv. 2025 Mar 31;15(13):9657-9661. doi: 10.1039/d4ra09021g. eCollection 2025 Mar 28. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40165921 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huang W-H, Zavalij PY, Isaacs L. Chiral recognition inside a chiral cucurbituril. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007;46:7425–7427. - PubMed
-
- Zehnacker A, Suhm MA. Chirality recognition between neutral molecules in the gas phase. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008;47:6970–6992. - PubMed
-
- Thomas CM, Ward TR. Artificial metalloenzymes: proteins as hosts for enantioselective catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2005;34:337–346. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

