Intranasal delivery of NGF rescues hearing impairment in aged SAMP8 mice
- PMID: 37704645
- PMCID: PMC10499813
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-023-06100-8
Intranasal delivery of NGF rescues hearing impairment in aged SAMP8 mice
Abstract
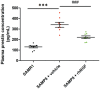
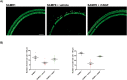
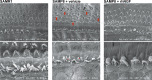
Hearing loss impacts the quality of life and affects communication resulting in social isolation and reduced well-being. Despite its impact on society and economy, no therapies for age-related hearing loss are available so far. Loss of mechanosensory hair cells of the cochlea is a common event of hearing loss in humans. Studies performed in birds demonstrating that they can be replaced following the proliferation and transdifferentiation of supporting cells, strongly pointed out on HCs regeneration as the main focus of research aimed at hearing regeneration. Neurotrophins are growth factors involved in neuronal survival, development, differentiation, and plasticity. NGF has been involved in the interplay between auditory receptors and efferent innervation in the cochlea during development. During embryo development, both NGF and its receptors are highly expressed in the inner ears. It has been reported that NGF is implicated in the differentiation of auditory gangliar and hair cells. Thus, it has been proposed that NGF administration can decrease neuronal damage and prevent hearing loss. The main obstacle to the development of hearing impairment therapy is that efficient means of delivery for selected drugs to the cochlea are missing. Herein, in this study NGF was administered by the intranasal route. The first part of the study was focused on a biodistribution study, which showed the effective delivery in the cochlea; while the second part was focused on analyzing the potential therapeutic effect of NGF in senescence-accelerated prone strain 8 mice. Interestingly, intranasal administration of NGF resulted protective in counteracting hearing impairment in SAMP8 mice, ameliorating hearing performances (analyzed by auditory brainstem responses and distortion product otoacoustic emission) and hair cells morphology (analyzed by microscopy analysis). The results obtained were encouraging indicating that the neurotrophin NGF was efficiently delivered to the inner ear and that it was effective in counteracting hearing loss.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
LB, FC, PC, AA, and MA are employees of Dompé Farmaceutici S.p.A., Italy. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

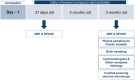
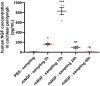
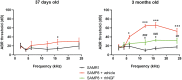
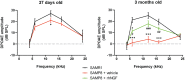

References
-
- Huddle MG, Goman AM, Kernizan FC, Foley DM, Price C, Frick KD, et al. The economic impact of adult hearing loss: a systematic review. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017;143:1040–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

