Membranous Nephropathy After Exposure to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
- PMID: 37705909
- PMCID: PMC10496011
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2023.06.001
Membranous Nephropathy After Exposure to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
Figures
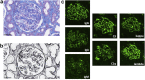
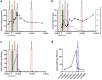
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

