Increased interhemispheric functional connectivity during non-dominant hand movement in right-handed subjects
- PMID: 37705959
- PMCID: PMC10495657
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107592
Increased interhemispheric functional connectivity during non-dominant hand movement in right-handed subjects
Abstract
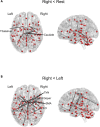
Hand preference is one of the behavioral expressions of lateralization in the brain. Previous fMRI studies showed the activation in several regions including the motor cortex and the cerebellum during single-hand movement. However, functional connectivity related to hand preference has not been investigated. Here, we used the generalized psychophysiological interaction (gPPI) approach to investigate the alteration of functional connectivity during single-hand movement from the resting state in right-hand subjects. The functional connectivity in interhemispheric motor-related regions including the supplementary motor area, the precentral gyrus, and the cerebellum was significantly increased during non-dominant hand movement, while functional connectivity was not increased during dominant hand movement. The general linear model (GLM) showed activation in contralateral supplementary motor area, contralateral precentral gyrus, and ipsilateral cerebellum during right- or left-hand movement. These results indicate that a combination of GLM and gPPI analysis can detect the lateralization of hand preference more clearly.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Neuroscience; Techniques in neuroscience.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Ciavarro M., Grande E., Pavone L., Bevacqua G., De Angelis M., di Russo P., Morace R., Committeri G., Grillea G., Bartolo M., et al. Pre-surgical fMRI Localization of the Hand Motor Cortex in Brain Tumors: Comparison Between Finger Tapping Task and a New Visual-Triggered Finger Movement Task. Front. Neurol. 2021;12 doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.658025. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

