Circulating extracellular vesicles in human cardiorenal syndrome promote renal injury in a kidney-on-chip system
- PMID: 37707956
- PMCID: PMC10721327
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.165172
Circulating extracellular vesicles in human cardiorenal syndrome promote renal injury in a kidney-on-chip system
Abstract
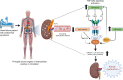
BACKGROUNDCardiorenal syndrome (CRS) - renal injury during heart failure (HF) - is linked to high morbidity. Whether circulating extracellular vesicles (EVs) and their RNA cargo directly impact its pathogenesis remains unclear.METHODSWe investigated the role of circulating EVs from patients with CRS on renal epithelial/endothelial cells using a microfluidic kidney-on-chip (KOC) model. The small RNA cargo of circulating EVs was regressed against serum creatinine to prioritize subsets of functionally relevant EV-miRNAs and their mRNA targets investigated using in silico pathway analysis, human genetics, and interrogation of expression in the KOC model and in renal tissue. The functional effects of EV-RNAs on kidney epithelial cells were experimentally validated.RESULTSRenal epithelial and endothelial cells in the KOC model exhibited uptake of EVs from patients with HF. HF-CRS EVs led to higher expression of renal injury markers (IL18, LCN2, HAVCR1) relative to non-CRS EVs. A total of 15 EV-miRNAs were associated with creatinine, targeting 1,143 gene targets specifying pathways relevant to renal injury, including TGF-β and AMPK signaling. We observed directionally consistent changes in the expression of TGF-β pathway members (BMP6, FST, TIMP3) in the KOC model exposed to CRS EVs, which were validated in epithelial cells treated with corresponding inhibitors and mimics of miRNAs. A similar trend was observed in renal tissue with kidney injury. Mendelian randomization suggested a role for FST in renal function.CONCLUSIONPlasma EVs in patients with CRS elicit adverse transcriptional and phenotypic responses in a KOC model by regulating biologically relevant pathways, suggesting a role for EVs in CRS.TRIAL REGISTRATIONClinicalTrials.gov NCT03345446.FUNDINGAmerican Heart Association (AHA) (SFRN16SFRN31280008); National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (1R35HL150807-01); National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (UH3 TR002878); and AHA (23CDA1045944).
Keywords: Cardiology; Fibrosis; Heart failure; Nephrology; Noncoding RNAs.
Figures







References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

