Measuring the efficacy of a vaccine during an epidemic
- PMID: 37708163
- PMCID: PMC10501570
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0290652
Measuring the efficacy of a vaccine during an epidemic
Abstract
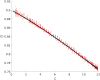
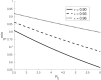
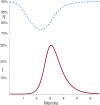
The urgency to develop vaccines during the COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in the acceleration of clinical trials. Specifically, a broad spectrum of efficacy levels has been reported for various vaccines based on phase III cohort studies. Our study demonstrates that conducting large cohort phase III clinical trials during the peak of an epidemic leads to a significant underestimation of vaccine efficacy, even in the absence of confounding factors. Furthermore, we find that this underestimation increases with the proportion of infectious individuals in the population during the experiment and the severity of the epidemic, as measured by its basic reproduction number.
Copyright: © 2023 Scala, Cavallo. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Draft landscape and tracker of COVID-19 candidate vaccines; 2021. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/draft-landscape-of-covid-19-cand....
-
- Halloran ME, Longini IM, Struchiner CJ. Design and analysis of vaccine studies. Statistics for biology and health. New York: Springer; 2010.
-
- Last JM, Association IE, editors. A dictionary of epidemiology. 4th ed. New York: Oxford University Press; 2001.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

