IL-33 Expression Is Lower in Current Smokers at both Transcriptomic and Protein Levels
- PMID: 37708400
- PMCID: PMC10867944
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202210-1881OC
IL-33 Expression Is Lower in Current Smokers at both Transcriptomic and Protein Levels
Abstract
Rationale: IL-33 is a proinflammatory cytokine thought to play a role in the pathogenesis of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). A recent clinical trial using an anti-IL-33 antibody showed a reduction in exacerbation and improved lung function in ex-smokers but not current smokers with COPD. Objectives: This study aimed to understand the effects of smoking status on IL-33. Methods: We investigated the association of smoking status with the level of gene expression of IL-33 in the airways in eight independent transcriptomic studies of lung airways. Additionally, we performed Western blot analysis and immunohistochemistry for IL-33 in lung tissue to assess protein levels. Measurements and Main Results: Across the bulk RNA-sequencing datasets, IL-33 gene expression and its signaling pathway were significantly lower in current versus former or never-smokers and increased upon smoking cessation (P < 0.05). Single-cell sequencing showed that IL-33 is predominantly expressed in resting basal epithelial cells and decreases during the differentiation process triggered by smoke exposure. We also found a higher transitioning of this cellular subpopulation into a more differentiated cell type during chronic smoking, potentially driving the reduction of IL-33. Protein analysis demonstrated lower IL-33 levels in lung tissue from current versus former smokers with COPD and a lower proportion of IL-33-positive basal cells in current versus ex-smoking controls. Conclusions: We provide strong evidence that cigarette smoke leads to an overall reduction in IL-33 expression in transcriptomic and protein level, and this may be due to the decrease in resting basal cells. Together, these findings may explain the clinical observation that a recent antibody-based anti-IL-33 treatment is more effective in former than current smokers with COPD.
Keywords: COPD; IL-33; basal cell; cigarette smoke; gene expression.
Figures
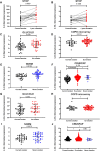
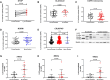

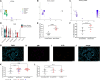
Comment in
-
Uncovering the Complexities of IL-33 Signaling in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023 Nov 15;208(10):1015-1016. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202309-1611ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023. PMID: 37792423 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Celli BR, Wedzicha JA. Update on clinical aspects of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med . 2019;381:1257–1266. - PubMed
-
- Barnes PJ, Burney PG, Silverman EK, Celli BR, Vestbo J, Wedzicha JA, et al. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers . 2015;1:15076. - PubMed
-
- Schmitz J, Owyang A, Oldham E, Song Y, Murphy E, McClanahan TK, et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity . 2005;23:479–490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

