Amivantamab plus lazertinib in osimertinib-relapsed EGFR-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a phase 1 trial
- PMID: 37710001
- PMCID: PMC10579096
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-023-02554-7
Amivantamab plus lazertinib in osimertinib-relapsed EGFR-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a phase 1 trial
Abstract
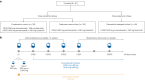
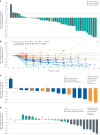
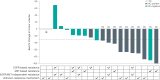
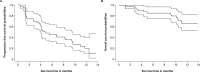
Patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) often develop resistance to current standard third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs); no targeted treatments are approved in the osimertinib-relapsed setting. In this open-label, dose-escalation and dose-expansion phase 1 trial, the potential for improved anti-tumor activity by combining amivantamab, an EGFR-MET bispecific antibody, with lazertinib, a third-generation EGFR TKI, was evaluated in patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC whose disease progressed on third-generation TKI monotherapy but were chemotherapy naive (CHRYSALIS cohort E). In the dose-escalation phase, the recommended phase 2 combination dose was established; in the dose-expansion phase, the primary endpoints were safety and overall response rate, and key secondary endpoints included progression-free survival and overall survival. The safety profile of amivantamab and lazertinib was generally consistent with previous experience of each agent alone, with 4% experiencing grade ≥3 events; no new safety signals were identified. In an exploratory cohort of 45 patients who were enrolled without biomarker selection, the primary endpoint of investigator-assessed overall response rate was 36% (95% confidence interval, 22-51). The median duration of response was 9.6 months, and the median progression-free survival was 4.9 months. Next-generation sequencing and immunohistochemistry analyses identified high EGFR and/or MET expression as potential predictive biomarkers of response, which will need to be validated with prospective assessment. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT02609776 .
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
B.C.C.: consulting or advisory role (Novartis, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Roche, Bristol Myers Squibb, Ono Pharmaceutical, Yuhan, Pfizer, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Takeda, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Medpacto, Blueprint Medicines, KANAPH Therapeutics, BridgeBio, Cyrus Therapeutics, Guardant Health and Oscotec); board of directors (Interpark Bio Convergence and J INTS BIO); research funding (Novartis, Bayer, AstraZeneca, MOGAM Institute, Dong-A ST, Champions Oncology, Janssen, Yuhan, Ono Pharmaceutical, Dizal Pharma, Merck Sharp & Dohme, AbbVie, Medpacto, GI Innovation, Eli Lilly, Blueprint Medicines and Interpark Bio Convergence); royalties (Champions Oncology); stock ownership (TheraCanVac, Gencurix, BridgeBio, KANAPH Therapeutics, Cyrus Therapeutics, Interpark Bio Convergence and J INTS BIO); founder (DAAN Biotherapeutics). D.-W.K.: travel, accommodations and expenses (Daiichi Sankyo and Amgen); research funding to institution (Alpha Biopharma, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, Hanmi, Janssen, Merus, Mirati Therapeutics, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Ono Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, Takeda, TP Therapeutics, Xcovery, Yuhan, Boehringer Ingelheim, Amgen and Daiichi Sankyo). A.I.S.: consulting or advisory role (Incyte, Amgen, Novartis, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, Mirati Therapeutics, Gritstone Oncology, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Takeda and Janssen); consulting or advisory role for institution (Array BioPharma, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, Merck and Bristol Myers Squibb); stock ownership (Eli Lilly); honoraria (CytomX Therapeutics, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, Merck, Takeda, Amgen, Janssen, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb and Bayer); research funding (LAM Therapeutics); research funding to institution (Roche, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Astellas Pharma, MedImmune, Novartis, Newlink Genetics, Incyte, AbbVie, Ignyta, LAM Therapeutics, Trovagene, Takeda, Macrogenics, CytomX Therapeutics, Astex Pharmaceuticals, Bristol Myers Squibb, LOXO Oncology, Arch Therapeutics, Gritstone Oncology, Plexxikon, Amgen, Daiichi Sankyo, ADC Therapeutics, Janssen, Mirati Therapeutics, Rubius and Synthekine); leadership role for institution (NEXT Oncology Virginia). J.E.G.: consulting or advisory role (AstraZeneca and Atara Biotherapeutics); honoraria (Bristol Myers Squibb and Celgene); speakers’ bureau (Bristol Myers Squibb); research funding to institution (Janssen); travel, accommodations and expenses (Atara Biotherapeutics, Bristol Myers Squibb and Celgene). E.B.H.: consulting or advisory role (Janssen, Revolution Medicines, and Ellipses Pharmaceuticals); research funding to institution (Revolution Medicines). S.-W.K.: consulting or advisory role (AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Ono Pharmaceutical, Bristol Myers Squibb, Amgen and Boehringer Ingelheim); speakers’ bureau (Boehringer Ingelheim and Amgen); research funding (AstraZeneca). R.E.S.: consulting or advisory role (AstraZeneca, EMD Serono, Blueprint Medicines, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Janssen Oncology, Macrogenics, Sanofi Aventis, Regeneron and Mirati Therapeutics); travel, accommodations and expenses (AstraZeneca); honoraria (AstraZeneca and Amgen); research funding to institution (Bristol Myers Squibb and MedImmune); research funding (Merck and AstraZeneca). E.K.C.: no relationships to disclose. K.H.L.: no relationships to disclose. A.M.: consulting or advisory boards (Janssen, Merck, Takeda, GSK and Genmab); honoraria (Chugai, Novartis Oncology, Faron Pharmaceuticals, Bayer and Janssen); expenses (Amgen and LOXO Oncology). J.-S.L.: consulting or advisory role (AstraZeneca and Ono Pharmaceutical). J.-Y.H.: consulting or advisory role (MSD Oncology, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Takeda and Pfizer); honoraria (Roche, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb and Takeda); research funding (Roche, Pfizer, Ono Pharmaceutical and Takeda). M.N.: consulting or advisory role (AstraZeneca, Caris Life Sciences, Daiichi Sankyo, Takeda, Novartis, EMD Serono, Pfizer, Eli Lilly, Genentech and Janssen); speakers’ bureau (Takeda and Blueprint Medicines); travel support (AnHeart Therapeutics). J.K.S.: consulting or advisory role (AstraZeneca, Janssen Oncology, Navire, Pfizer, Regeneron, Medscape and Takeda). S.-H.I.O.: advisory role (Elevation Oncology); stock ownership (Turning Point Therapeutics and Elevation Oncology); honorarium (Pfizer); advisory fees (BeiGene, Roche/Genentech, AstraZeneca, Takeda/ARIAD, Pfizer, Caris Life Science, Janssen, Daiichi Sankyo and Eli Lilly). P.L., J.M.B., J.C.C., A.R., G.G., J.X., M.T. and R.E.K.: employment and stock ownership (Johnson & Johnson). K.P.: consulting or advisory role (AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Ono Pharmaceutical, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Blueprint Medicines, Amgen, Merck, LOXO Oncology, AbbVie, Daiichi Sankyo, Boehringer Ingelheim, Johnson & Johnson, Eisai and Puma Biotechnology); speakers’ bureau (Boehringer Ingelheim and AZD); and research funding (AstraZeneca and Merck Sharp & Dohme).
Figures
References
-
- Rosell R, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:239–246. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70393-X. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

