Effect of silymarin on the relative gene expressions of some inflammatory cytokines in the liver of CCl4-intoxicated male rats
- PMID: 37710007
- PMCID: PMC10502111
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-42250-7
Effect of silymarin on the relative gene expressions of some inflammatory cytokines in the liver of CCl4-intoxicated male rats
Abstract
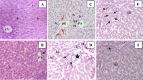
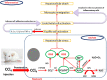
The intensive exposure of the liver cells to any type of noxae, such as viruses, drugs, alcohols, and xenobiotics could induce hepatic inflammation through the upregulation of gene expression of several fibrotic and inflammatory mediators. So, our study assessed the role of silymarin on the inflammatory response induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) as an example of xenobiotics on liver tissues in male rats. Forty-eight Wister male rats (weight: 130 ± 10) were housed for 14 days and then divided randomly into six groups: control, SLY: rats received only silymarin orally for 12 weeks (daily), CO: rats were injected with corn oil for 8 weeks (3 times weekly), CCl4: rats were injected with CCl4 solubilized in corn oil for 8 weeks (day by day), Treated: rats received silymarin for 4 weeks after CCl4 injection, Protected: rats received silymarin for 4 weeks before and 8 weeks during CCl4 injection. When the treatment period for the rats was over, they underwent scarification after anesthesia. Then, the sera were extracted from the collected blood for the determination of irisin levels, liver functions, and lipid profiles. Liver tissues were separated for the histopathological examinations, the determination of oxidative stress (OS) parameters content, and the relative gene expression of inflammatory cytokines; nuclear factor kappa (NF)-κB, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-6, cyclooxygenase (COX)-2, and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β). The findings showed that silymarin reduced liver inflammation by overcoming the OS process and inflammatory cytokines production which was stimulated by CCl4. These results were confirmed by histopathology of liver tissues.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Alternanthera brasiliana L. extract alleviates carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury and fibrotic changes in mice: Role of matrix metalloproteinases and TGF-β/Smad axis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Mar 1;303:115992. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115992. Epub 2022 Dec 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36509261
-
Beneficial Effects of Silymarin After the Discontinuation of CCl4-Induced Liver Fibrosis.J Med Food. 2016 Aug;19(8):789-97. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2015.0104. Epub 2016 Jul 21. J Med Food. 2016. PMID: 27441792
-
Antifibrotic effect of meloxicam in rat liver: role of nuclear factor kappa B, proinflammatory cytokines, and oxidative stress.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016 Sep;389(9):971-83. doi: 10.1007/s00210-016-1263-1. Epub 2016 May 31. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27245167
-
Hepatoprotective activity of ethanolic extract of Salix subserrata against CCl4-induced chronic hepatotoxicity in rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Jul 29;16:263. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1238-2. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 27473536 Free PMC article.
-
Silymarin and Inflammation: Food for Thoughts.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jan 14;13(1):98. doi: 10.3390/antiox13010098. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38247522 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The clinical anti-inflammatory effects and underlying mechanisms of silymarin.iScience. 2024 Oct 9;27(11):111109. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111109. eCollection 2024 Nov 15. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39507256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nephroprotective Effects of Fraxinus Hookeri Wenz. Against Renal Toxicity and DNA Oxidative Damages Induced by CCl4 in Rats.ChemistryOpen. 2025 Aug;14(8):e202400515. doi: 10.1002/open.202400515. Epub 2025 Jun 16. ChemistryOpen. 2025. PMID: 40518992 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Nutraceutical Potential of Carduus marianus: Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effects in Paracetamol-Induced Hepatotoxicity and GC-MS Analysis.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Jul 18;13(7):e70474. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70474. eCollection 2025 Jul. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40688605 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Effect of Melatonin on CCl4-Induced Fibrotic Liver Model by Modulating Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and TGF-β1 Signaling Pathway in Pinealectomized Rats.Inflammation. 2025 Jun;48(3):1093-1108. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02101-7. Epub 2024 Jul 15. Inflammation. 2025. PMID: 39007940 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the therapeutic potential of unexplored phytocompounds as hepatoprotective agents through integration of network pharmacology and in-silico analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 11;15(1):8425. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-92868-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40069278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seitz HK, et al. Alcoholic liver disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018;4:1–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

