Protein-lipid charge interactions control the folding of outer membrane proteins into asymmetric membranes
- PMID: 37710048
- PMCID: PMC10695831
- DOI: 10.1038/s41557-023-01319-6
Protein-lipid charge interactions control the folding of outer membrane proteins into asymmetric membranes
Abstract
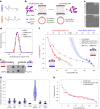
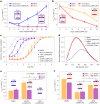
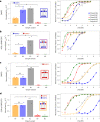
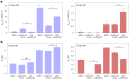
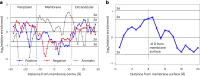
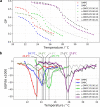
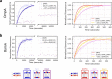
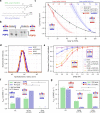
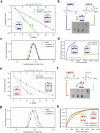
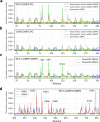
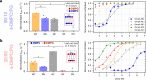
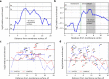
Biological membranes consist of two leaflets of phospholipid molecules that form a bilayer, each leaflet comprising a distinct lipid composition. This asymmetry is created and maintained in vivo by dedicated biochemical pathways, but difficulties in creating stable asymmetric membranes in vitro have restricted our understanding of how bilayer asymmetry modulates the folding, stability and function of membrane proteins. In this study, we used cyclodextrin-mediated lipid exchange to generate liposomes with asymmetric bilayers and characterize the stability and folding kinetics of two bacterial outer membrane proteins (OMPs), OmpA and BamA. We found that excess negative charge in the outer leaflet of a liposome impedes their insertion and folding, while excess negative charge in the inner leaflet accelerates their folding relative to symmetric liposomes with the same membrane composition. Using molecular dynamics, mutational analysis and bioinformatics, we identified a positively charged patch critical for folding and stability. These results rationalize the well-known 'positive-outside' rule of OMPs and suggest insights into the mechanisms that drive OMP folding and assembly in vitro and in vivo.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Protein-induced membrane asymmetry modulates OMP folding kinetics and stability.Faraday Discuss. 2025 Aug 13;259(0):579-596. doi: 10.1039/d4fd00180j. Faraday Discuss. 2025. PMID: 40338084 Free PMC article.
-
OmpA Specifically Modulates the Activity of Enzymes that Reside in the Crowded Bacterial Outer Membrane.J Mol Biol. 2025 Oct 1;437(19):169346. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2025.169346. Epub 2025 Jul 14. J Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40669592 Free PMC article.
-
The role of membrane destabilisation and protein dynamics in BAM catalysed OMP folding.Nat Commun. 2021 Jul 7;12(1):4174. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24432-x. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34234105 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Insights into the Cholesterol-Mediated Modulation of Membrane Function Through Molecular Dynamics Simulations.Membranes (Basel). 2025 Jun 8;15(6):173. doi: 10.3390/membranes15060173. Membranes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40559352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors that influence parents' and informal caregivers' views and practices regarding routine childhood vaccination: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 27;10(10):CD013265. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013265.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34706066 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Research Progress of Phospholipid Vesicles in Biological Field.Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 19;14(12):1628. doi: 10.3390/biom14121628. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kingdom-specific lipid unsaturation calibrates sequence evolution in membrane arm subunits of eukaryotic respiratory complexes.Nat Commun. 2025 Feb 27;16(1):2044. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57295-7. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40016208 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into Liposomal and Gel-Based Formulations for Dermatological Treatments.Gels. 2025 Mar 26;11(4):245. doi: 10.3390/gels11040245. Gels. 2025. PMID: 40277680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
POTRA domains of the TamA insertase interact with the outer membrane and modulate membrane properties.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jul 9;121(28):e2402543121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2402543121. Epub 2024 Jul 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38959031 Free PMC article.
-
Seeing is believing: Illuminating the Gram-negative outer membrane with molecular dynamics simulations.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2024 Aug;87:102828. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2024.102828. Epub 2024 May 8. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2024. PMID: 38723580 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

