International consensus recommendations for the identification and treatment of tuberous sclerosis complex-associated neuropsychiatric disorders (TAND)
- PMID: 37710171
- PMCID: PMC10503032
- DOI: 10.1186/s11689-023-09500-1
International consensus recommendations for the identification and treatment of tuberous sclerosis complex-associated neuropsychiatric disorders (TAND)
Abstract
Background: Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) is associated with a wide range of physical manifestations for which international clinical recommendations for diagnosis and management have been established. TSC is, however, also associated with a wide range of TSC-Associated Neuropsychiatric Disorders (TAND) that are typically under-identified and under-treated yet associated with a profound burden of disease. The contemporary evidence base for the identification and treatment of TAND is much more limited and, to date, consensus recommendations for the diagnosis and management of TAND have also been limited and non-specific.
Methods: The TANDem project was launched with an international, interdisciplinary, and participatory consortium of 24 individuals, including TSC family representatives, from all World Health Organization (WHO) regions but one. One of the aims of the TANDem project was to generate consensus recommendations for the identification and treatment of TAND. At the time of this project, no internationally adopted standard methodology and methodological checklists existed for the generation of clinical practice recommendations. We therefore developed our own systematic procedure for evidence review and consensus-building to generate evidence-informed consensus recommendations of relevance to the global TSC community.
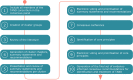
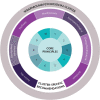
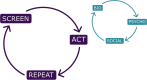
Results: At the heart of the consensus recommendations are ten core principles surrounded by cluster-specific recommendations for each of the seven natural TAND clusters identified in the literature (autism-like, dysregulated behavior, eat/sleep, mood/anxiety, neuropsychological, overactive/impulsive, and scholastic) and a set of wraparound psychosocial cluster recommendations. The overarching recommendation is to "screen" for TAND at least annually, to "act" using appropriate next steps for evaluation and treatment, and to "repeat" the process to ensure early identification and early intervention with the most appropriate biological, psychological, and social evidence-informed approaches to support individuals with TSC and their families.
Conclusions: The consensus recommendations should provide a systematic framework to approach the identification and treatment of TAND for health, educational, social care teams and families who live with TSC. To ensure global dissemination and implementation of these recommendations, partnerships with the international TSC community will be important. One of these steps will include the generation of a "TAND toolkit" of "what to seek" and "what to do" when difficulties are identified in TAND clusters.
Keywords: Consensus recommendations; Education; Mental health; Neurodevelopmental disability; Rare genetic disorders; TAND; Tuberous sclerosis complex.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
PJdV was a study steering committee member of three phase III trials in TSC sponsored by Novartis, was on the scientific advisory group of the TOSCA international disease registry sponsored by Novartis, and has provided consultancy to GW Pharma. SB is funded by Cerebra to investigate sleep and behavior in rare genetic syndromes, including TSC. AVE is on the scientific advisory board and received grant support from Jazz Pharmaceuticals. JC receives grant funding from the NIH and the Department of Defense for projects related to TSC. PD receives partial salary support from the NIH for participation in studies related to TSC, as well as from Aucta Pharmaceuticals for a study of topical sirolimus for facial angiofibromas in TSC and Marinus Pharmaceuticals for a study of ganaxolone for TSC‑related epilepsy. CS receives salary support from the TSC Alliance, a non‑profit organization that reports revenue from individual donors and corporations including Greenwich Biosciences, GW Pharma, Mallinckrodt, Nobelpharma, Novartis, Ovid, UCB, and Upsher‑Smith. DAK reports grants from the National Institutes of Health (NINDS) during the conduct of the study as well as the personal fees from Novartis Pharmaceuticals, personal fees from Greenwich Bioscience, grants from Marinus Pharmaceuticals, personal fees from Nobelpharma America, personal fees from REGENXBIO, and grants and non‑financial support from TSC Alliance outside the submitted work. MS reports grant support from Novartis, Biogen, Astellas, Aeovian, Bridgebio, and Aucta and has served on Scientific Advisory Boards for Novartis, Roche, Regenxbio, SpringWorks Therapeutics, Jaguar Therapeutics, and Alkermes. ACJ was on the scientific advisory group of the TOSCA international disease registry sponsored by Novartis and has provided consultancy to GW Pharma. The remaining authors declared no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Northrup H, Aronow ME, Bebin EM, Bissler J, Darling TN, de Vries PJ, et al. Updated international tuberous sclerosis complex diagnostic criteria and surveillance and management recommendations. Pediatr Neurol. 2021;123:50–66. - PubMed
-
- Henske EP, Józwiak S, Kingswood JC, Sampson JR, Thiele EA. Tuberous sclerosis complex. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2016;2:16035. - PubMed
-
- Curatolo P, Moavero R, de Vries PJ. Neurological and neuropsychiatric aspects of tuberous sclerosis complex. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14(7):733–745. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

