Vancomycin and daptomycin dosing recommendations in patients receiving home hemodialysis using Monte Carlo simulation
- PMID: 37710245
- PMCID: PMC10500909
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-023-03314-y
Vancomycin and daptomycin dosing recommendations in patients receiving home hemodialysis using Monte Carlo simulation
Abstract
Background: Few drug dosing recommendations for patients receiving home hemodialysis (HHD) have been published which has hindered the adoption of HHD. HHD regimens vary widely and differ considerably from conventional, thrice weekly, in-center hemodialysis in terms of treatment frequency, duration and blood and dialysate flow rates. Consequently, vancomycin and daptomycin clearances in HHD are also likely to be different, consequently HHD dosing regimens must be developed to ensure efficacy and minimize toxicity when these antibiotics are used. Many HHD regimens are used clinically, this study modeled ten common HHD regimens and determined optimal vancomycin and daptomycin dosing for each HHD regimen.
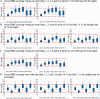
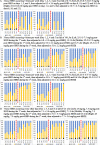
Methods: Monte Carlo simulations using pharmacokinetic data derived from the literature and demographic data from a large HHD program treating patients with end stage kidney disease were incorporated into a one-compartment pharmacokinetic model. Virtual vancomycin and daptomycin doses were administered post-HHD and drug exposures were determined in 5,000 virtual patients receiving ten different HHD regimens. Serum concentration monitoring with subsequent dose changes was incorporated into the vancomycin models. Pharmacodynamic target attainment rates were determined for each studied dose. The lowest possible doses that met predefined targets in virtual patients were chosen as optimal doses.
Results: HHD frequency, total dialysate volumes and HHD durations influenced drug exposure and led to different dosing regimens to meet targets. Antibiotic dosing regimens were identified that could meet targets for 3- and 7-h HHD regimens occurring every other day or 4-5 days/week. HHD regimens with 3-day interdialytic periods required higher doses prior to the 3-day period. The addition of vancomycin serum concentration monitoring allowed for calculation of necessary dosing changes which increased the number of virtual subjects meeting pharmacodynamic targets.
Conclusions: Doses of vancomycin and daptomycin that will meet desired pharmacodynamic targets in HHD are dependent on patient and HHD-specific factors. Doses used in conventional thrice weekly hemodialysis are unlikely to meet treatment goals. The antibiotic regimens paired with the HHD parameters studied in this analysis are likely to meet goals but require clinical validation.
Keywords: Daptomycin; Home hemodialysis; Monte Carlo simulation; Pharmacodynamics; Pharmacokinetics; Renal disease; Vancomycin.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Mueller received grant funding from NxStage/Fresenius Medical Care AG & Co. to support this study. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation and Development of Vancomycin Dosing Schemes to Meet New AUC/MIC Targets in Intermittent Hemodialysis Using Monte Carlo Simulation Techniques.J Clin Pharmacol. 2021 Feb;61(2):211-223. doi: 10.1002/jcph.1727. Epub 2020 Aug 26. J Clin Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32851685
-
Use of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic principles to determine optimal administration of daptomycin in patients receiving standardized thrice-weekly hemodialysis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Apr;55(4):1677-83. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01224-10. Epub 2011 Jan 31. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21282429 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a vancomycin dosing approach for critically ill patients receiving hybrid hemodialysis using Monte Carlo simulation.SAGE Open Med. 2018 May 11;6:2050312118773257. doi: 10.1177/2050312118773257. eCollection 2018. SAGE Open Med. 2018. PMID: 29780587 Free PMC article.
-
Daptomycin dosing strategies in patients receiving thrice-weekly intermittent hemodialysis.Ann Pharmacother. 2013 Oct;47(10):1342-7. doi: 10.1177/1060028013503110. Ann Pharmacother. 2013. PMID: 24259698 Review.
-
Vancomycin dosing and monitoring for patients with end-stage renal disease receiving intermittent hemodialysis.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2015 Nov 1;72(21):1856-64. doi: 10.2146/ajhp150051. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2015. PMID: 26490819 Review.
References
-
- United States Renal Data System . 2021 USRDS Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Bethesda: National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous