The roles of different microRNAs in the regulation of cholesterol in viral hepatitis
- PMID: 37710249
- PMCID: PMC10500852
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-023-01250-w
The roles of different microRNAs in the regulation of cholesterol in viral hepatitis
Erratum in
-
Correction: The roles of different microRNAs in the regulation of cholesterol in viral hepatitis.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Sep 21;21(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01325-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37735676 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
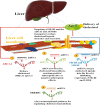
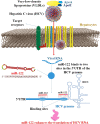
Cholesterol plays a significant role in stabilizing lipid or membrane rafts, which are specific cellular membrane structures. Cholesterol is involved in numerous cellular processes, including regulating virus entry into the host cell. Multiple viruses have been shown to rely on cholesterol for virus entry and/or morphogenesis. Research indicates that reprogramming of the host's lipid metabolism is associated with hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections in the progression to severe liver disease for viruses that cause chronic hepatitis. Moreover, knowing the precise mode of viral interaction with target cells sheds light on viral pathogenesis and aids in the development of vaccines and therapeutic targets. As a result, the area of cholesterol-lowering therapy is quickly evolving and has many novel antiviral targets and medications. It has been shown that microRNAs (miRNAs) either directly or indirectly target the viral genome, preventing viral replication. Moreover, miRNAs have recently been shown to be strong post-transcriptional regulators of the genes involved in lipid metabolism, particularly those involved in cholesterol homeostasis. As important regulators of lipid homeostasis in several viral infections, miRNAs have recently come to light. In addition, multiple studies demonstrated that during viral infection, miRNAs modulate several enzymes in the mevalonate/cholesterol pathway. As cholesterol metabolism is essential to the life cycle of viral hepatitis and other viruses, a sophisticated understanding of miRNA regulation may contribute to the development of a novel anti-HCV treatment. The mechanisms underlying the effectiveness of miRNAs as cholesterol regulators against viral hepatitis are explored in this review. Video Abstract.
Keywords: Cholesterol; Viral hepatitis; Viral infections; microRNAs.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Viral Hepatitis, Cholesterol Metabolism, and Cholesterol-Lowering Natural Compounds.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 31;23(7):3897. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073897. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptomic Analysis of Chronic Hepatitis B and C and Liver Cancer Reveals MicroRNA-Mediated Control of Cholesterol Synthesis Programs.mBio. 2015 Dec 8;6(6):e01500-15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01500-15. mBio. 2015. PMID: 26646011 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus and microRNAs: Complex interactions affecting hepatitis B virus replication and hepatitis B virus-associated diseases.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jun 28;21(24):7375-99. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7375. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26139985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex interactions between microRNAs and hepatitis B/C viruses.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Oct 7;20(37):13477-92. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13477. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25309078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging role of miRNA-122 in infectious diseases: Mechanisms and potential biomarkers.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Sep;249:154725. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154725. Epub 2023 Jul 27. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37544130 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in nanomaterial-based biosensor for periodontitis detection.J Biol Eng. 2024 Apr 18;18(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s13036-024-00423-6. J Biol Eng. 2024. PMID: 38637787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of dyslipidemia on HBsAg clearance in nucleos(t)ide analogues-experienced chronic hepatitis B patients treated with peginterferon alfa.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Nov 11;24(1):1273. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-10093-w. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39528941 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of the role of Niemann-pick C1 (NPC1) in viral infections and inhibition of viral infections through NPC1 inhibitor.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Dec 14;21(1):352. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01376-x. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 38098077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of lipids and lipids lowering drugs in human papillomavirus (HPV) and HPV-associated cancers.Infect Agent Cancer. 2025 Jan 28;20(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s13027-025-00635-5. Infect Agent Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39876011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A state-of-the-art review on the NRF2 in Hepatitis virus-associated liver cancer.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Nov 9;21(1):318. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01351-6. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37946175 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Huang B, Song B-l, Xu C. Cholesterol metabolism in cancer: mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Nat metabolism. 2020;2(2):132–41. - PubMed
-
- Hooper DR, et al. Endocrinological roles for testosterone in resistance exercise responses and adaptations. Sports Med. 2017;47:1709–20. - PubMed
-
- Zeng H, et al. Cholesterol and C-reactive protein prognostic score predicted prognosis of immune checkpoint inhibitors based interventional therapies for intermediate-to-advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;115:109651. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

