Hexarelin alleviates apoptosis on ischemic acute kidney injury via MDM2/p53 pathway
- PMID: 37710348
- PMCID: PMC10500723
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-023-01318-w
Hexarelin alleviates apoptosis on ischemic acute kidney injury via MDM2/p53 pathway
Abstract
Introduction: Hexarelin exhibits significant protection against organ injury in models of ischemia/reperfusion (I/R)-induced injury (IRI). Nevertheless, the impact of Hexarelin on acute kidney injury (AKI) and its underlying mechanism remains unclear. In this study, we investigated the therapeutic potential of Hexarelin in I/R-induced AKI and elucidated its molecular mechanisms.
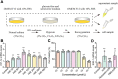
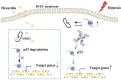
Methods: We assessed the protective effects of Hexarelin through both in vivo and in vitro experiments. In the I/R-induced AKI model, rats were pretreated with Hexarelin at 100 μg/kg/d for 7 days before being sacrificed 24 h post-IRI. Subsequently, kidney function, histology, and apoptosis were assessed. In vitro, hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R)-induced HK-2 cell model was used to investigate the impact of Hexarelin on apoptosis in HK-2 cells. Then, we employed molecular docking using a pharmmapper server and autodock software to identify potential target proteins of Hexarelin.
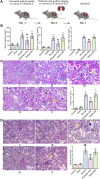
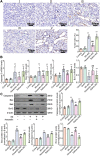
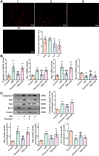
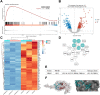
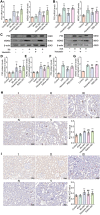
Results: In this study, rats subjected to I/R developed severe kidney injury characterized by tubular necrosis, tubular dilatation, increased serum creatinine levels, and cell apoptosis. However, pretreatment with Hexarelin exhibited a protective effect by mitigating post-ischemic kidney pathological changes, improving renal function, and inhibiting apoptosis. This was achieved through the downregulation of conventional apoptosis-related genes, such as Caspase-3, Bax and Bad, and the upregulation of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2. Consistent with the in vivo results, Hexarelin also reduced cell apoptosis in post-H/R HK-2 cells. Furthermore, our analysis using GSEA confirmed the essential role of the apoptosis pathway in I/R-induced AKI. Molecular docking revealed a strong binding affinity between Hexarelin and MDM2, suggesting the potential mechanism of Hexarelin's anti-apoptosis effect at least partially through its interaction with MDM2, a well-known negative regulator of apoptosis-related protein that of p53. To validate these findings, we evaluated the relative expression of MDM2 and p53 in I/R-induced AKI with or without Hexarelin pre-administration and observed a significant suppression of MDM2 and p53 by Hexarelin in both in vivo and in vitro experiments.
Conclusion: Collectively, Hexarelin was identified as a promising medication in protecting apoptosis against I/R-induced AKI.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Apoptosis; Hexarelin; Kidney ischemia–reperfusion injury; MDM2/p53.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Proximal Tubular Lats2 Ablation Exacerbates Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury (IRI)-Induced Renal Maladaptive Repair through the Upregulation of P53.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 17;24(20):15258. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015258. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894939 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology and experimental validation to investigate the mechanism of Nao-Ling-Su capsule in the treatment of ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 May 23;326:117958. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117958. Epub 2024 Feb 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38395179
-
Hypoxic mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate acute kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury via enhancing renal tubular autophagy.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Jun 28;12(1):367. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02374-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34183058 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Fc-Elabela-21 on renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice: Mediation of anti-apoptotic effect via Akt phosphorylation.Peptides. 2022 Jan;147:170682. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2021.170682. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Peptides. 2022. PMID: 34742787
-
p53-cyclophilin D mediates renal tubular cell apoptosis in ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019 Nov 1;317(5):F1311-F1317. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00072.2019. Epub 2019 Jul 24. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31339772 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Hesperetin attenuates ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury by regulating ferroptosis in mice.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2523573. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2523573. Epub 2025 Jun 29. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 40583332 Free PMC article.
-
The crosstalk of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and p53 in acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease.Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024 Nov;43(6):724-738. doi: 10.23876/j.krcp.23.344. Epub 2024 Nov 18. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024. PMID: 39558651 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

