Association between serum albumin to serum creatinine ratio and mortality risk in patients with heart failure
- PMID: 37710402
- PMCID: PMC10651659
- DOI: 10.1111/cts.13636
Association between serum albumin to serum creatinine ratio and mortality risk in patients with heart failure
Abstract
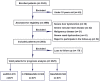
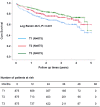
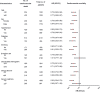
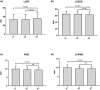
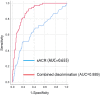
The aim of this study was to investigate the association between serum albumin to serum creatinine ratio (sACR) and the prognosis of heart failure (HF). In this single-center prospective cohort study, a total of 2625 patients with HF were enrolled between March 2012 and June 2017. All patients were divided into three groups according to the tertiles of sACR. Of 2625 patients, the mean age was 57.0 ± 14.3 years. During a median follow-up time of 23 months, 666 end point events occurred. Prognosis analysis indicated that the lowest sACR was significantly associated with higher mortality risk of HF (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.920, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.585-2.326, p < 0.001) when compared with the highest tertile. After adjusting for covariates including age, gender, diabetes, systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure, heart rate, total cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL-C, LDL-C, white blood cell count, hemoglobin, glycosylated hemoglobin, and β-blocker use, the HRs for mortality risk of HF was 1.513 (95% CI = 1.070-2.139, p = 0.019). Subgroup analysis indicated that the mortality risk of HF statistically significantly reduced with the rise in sACR in patients with no β-blocker use, patients with serum creatine less than 97 μmol/L. However, stratification by age, sex, history of hypertension, diabetes, and smoking, level of glycosylated hemoglobin, and albumin have no obvious effect on the association between sACR and the prognosis of HF. Additionally, patients with lower sACR displayed reduced left ventricular ejection fraction and increased left ventricular end-diastolic diameter. The discriminant power of sACR alone and in combination with age, gender, SBP, heart rate, and glycosylated hemoglobin were excellent with C statistic of 0.655 and 0.889, respectively. Lower sACR was an independent risk factor for mortality risk of HF.
© 2023 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Science published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no competing interests for this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between serum albumin creatinine ratio and all-cause mortality in intensive care unit patients with heart failure.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jul 4;11:1406294. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1406294. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39027002 Free PMC article.
-
The Prognostic Value of Blood Urea Nitrogen to Albumin Ratio on Patients with Heart Failure.Int Heart J. 2023 Nov 30;64(6):1010-1017. doi: 10.1536/ihj.23-383. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Int Heart J. 2023. PMID: 37967977
-
Association of Albumin-To-Creatinine Ratio With Diabetic Retinopathy Among US Adults (NHANES 2009-2016).Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2025 Jan;8(1):e70029. doi: 10.1002/edm2.70029. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2025. PMID: 39826101 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of serum albumin-to-creatinine ratio in patients with acute myocardial infarction: Results from the retrospective evaluation of acute chest pain study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Aug 28;99(35):e22049. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022049. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32871964 Free PMC article.
-
Home Based Cardiac Rehabilitation Participation Among Patients With Heart Failure.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2023 Dec;48(12):102013. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2023.102013. Epub 2023 Aug 5. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37544630 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between serum albumin creatinine ratio and all-cause mortality in intensive care unit patients with heart failure.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jul 4;11:1406294. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1406294. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39027002 Free PMC article.
-
Association of serum albumin-to-creatinine ratio with in-hospital mortality in patients with severe acute pancreatitis: a retrospective study.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Nov 11;24(1):401. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03493-4. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39529034 Free PMC article.
-
Association of serum creatinine-to-albumin ratio with 28-day all-cause mortality in older adults critically ill patients with sepsis: a retrospective analysis of the MIMIC-IV database.BMC Geriatr. 2025 Jul 2;25(1):477. doi: 10.1186/s12877-025-06093-3. BMC Geriatr. 2025. PMID: 40604550 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of serum albumin-creatinine ratio as a biomarker in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors.Immunotherapy. 2025 Jun;17(8):567-575. doi: 10.1080/1750743X.2025.2513850. Epub 2025 Jun 5. Immunotherapy. 2025. PMID: 40470574
-
Association between the serum albumin-creatinine ratio and 28-day intensive care unit mortality among patients with sepsis: a multicenter retrospective cohort study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Nov 5;11:1484370. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1484370. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39564496 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

