Biallelic missense variants in COG3 cause a congenital disorder of glycosylation with impairment of retrograde vesicular trafficking
- PMID: 37711075
- PMCID: PMC10873070
- DOI: 10.1002/jimd.12679
Biallelic missense variants in COG3 cause a congenital disorder of glycosylation with impairment of retrograde vesicular trafficking
Abstract
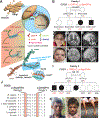
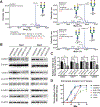
Biallelic variants in genes for seven out of eight subunits of the conserved oligomeric Golgi complex (COG) are known to cause recessive congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG) with variable clinical manifestations. COG3 encodes a constituent subunit of the COG complex that has not been associated with disease traits in humans. Herein, we report two COG3 homozygous missense variants in four individuals from two unrelated consanguineous families that co-segregated with COG3-CDG presentations. Clinical phenotypes of affected individuals include global developmental delay, severe intellectual disability, microcephaly, epilepsy, facial dysmorphism, and variable neurological findings. Biochemical analysis of serum transferrin from one family showed the loss of a single sialic acid. Western blotting on patient-derived fibroblasts revealed reduced COG3 and COG4. Further experiments showed delayed retrograde vesicular recycling in patient cells. This report adds to the knowledge of the COG-CDG network by providing collective evidence for a COG3-CDG rare disease trait and implicating a likely pathology of the disorder as the perturbation of Golgi trafficking.
Keywords: AOH/ROH analysis; congenital disorders of glycosylation; conserved oligomeric Golgi complex; family-based genomic analysis; retrograde vesicular transport.
© 2023 SSIEM.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
James R. Lupski has stock ownership in 23andMe, is a paid consultant for Genomics International, and is a co-inventor on multiple United States and European patents related to molecular diagnostics for inherited neuropathies, eye diseases, genomic disorders, and bacterial genomic fingerprinting. The Department of Molecular and Human Genetics at Baylor College of Medicine receives revenue from clinical genetic testing conducted at Baylor Genetics (BG); James R. Lupski serves on the Scientific Advisory Board (SAB) of BG. Ruizhi Duan, Dana Marafi1, Zhi-Jie Xia, Bobby G. Ng, Reza Maroofian, Farhana Taher Sumya, Ahmed K. Saad, Haowei Du, Jawid M. Fatih, Jill V. Hunter, Hasnaa M. Elbendary, Shahid M. Baig, Uzma Abdullah, Zafar Ali, Stephanie Efthymiou, David Murphy, Tadahiro Mitani, Marjorie A. Withers, Shalini N. Jhangiani, Zeynep Coban-Akdemir, Daniel G. Calame, Davut Pehlivan, Richard A. Gibbs, Jennifer E. Posey, Henry Houlden, Vladimir V. Lupashin, Maha S. Zaki and Hudson H. Freeze declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

