Intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics model based on abdominal ultrasound for predicting Ki-67 expression in patients with hepatocellular cancer
- PMID: 37711208
- PMCID: PMC10498123
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1209111
Intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics model based on abdominal ultrasound for predicting Ki-67 expression in patients with hepatocellular cancer
Abstract
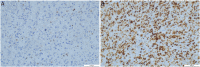
Background: Hepatocellular cancer (HCC) is one of the most common tumors worldwide, and Ki-67 is highly important in the assessment of HCC. Our study aimed to evaluate the value of ultrasound radiomics based on intratumoral and peritumoral tissues in predicting Ki-67 expression levels in patients with HCC.
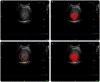
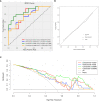
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of ultrasonic and clinical data from 118 patients diagnosed with HCC through histopathological examination of surgical specimens in our hospital between September 2019 and January 2023. Radiomics features were extracted from ultrasound images of both intratumoral and peritumoral regions. To select the optimal features, we utilized the t-test and the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO). We compared the area under the curve (AUC) values to determine the most effective modeling method. Subsequently, we developed four models: the intratumoral model, the peritumoral model, combined model #1, and combined model #2.
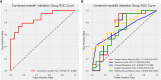
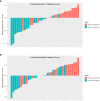
Results: Of the 118 patients, 64 were confirmed to have high Ki-67 expression while 54 were confirmed to have low Ki-67 expression. The AUC of the intratumoral model was 0.796 (0.649-0.942), and the AUC of the peritumoral model was 0.772 (0.619-0.926). Furthermore, combined model#1 yielded an AUC of 0.870 (0.751-0.989), and the AUC of combined model#2 was 0.762 (0.605-0.918). Among these models, combined model#1 showed the best performance in terms of AUC, accuracy, F1-score, and decision curve analysis (DCA).
Conclusion: We presented an ultrasound radiomics model that utilizes both intratumoral and peritumoral tissue information to accurately predict Ki-67 expression in HCC patients. We believe that incorporating both regions in a proper manner can enhance the diagnostic performance of the prediction model. Nevertheless, it is not sufficient to include both regions in the region of interest (ROI) without careful consideration.
Keywords: Ki-67 Antigen; computer assisted diagnosis; hepatocellular cancer; machine learning; radiomics; ultrasonography.
Copyright © 2023 Qian, Shen, Zhou and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prediction of Ki-67 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma with machine learning models based on intratumoral and peritumoral radiomic features.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025 May 15;17(5):104172. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.104172. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40487953 Free PMC article.
-
Intratumoral and Peritumoral Analysis of Mammography, Tomosynthesis, and Multiparametric MRI for Predicting Ki-67 Level in Breast Cancer: a Radiomics-Based Study.Mol Imaging Biol. 2022 Aug;24(4):550-559. doi: 10.1007/s11307-021-01695-w. Epub 2021 Dec 13. Mol Imaging Biol. 2022. PMID: 34904187
-
Development of an interpretable machine learning model for Ki-67 prediction in breast cancer using intratumoral and peritumoral ultrasound radiomics features.Front Oncol. 2023 Nov 17;13:1290313. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1290313. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38044998 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of radiomics in predicting Ki-67 and cytokeratin 19 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2024 Jan 3;13:1323534. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1323534. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38234405 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress in multimodal radiomics of rectal cancer tumors and peritumoral regions in MRI.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025 May 31. doi: 10.1007/s00261-025-04965-1. Online ahead of print. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025. PMID: 40448847 Review.
Cited by
-
Computed tomography radiomics combined with clinical parameters for hepatocellular carcinoma differentiation: a machine learning investigation.Pol J Radiol. 2025 Mar 24;90:e140-e150. doi: 10.5114/pjr/200631. eCollection 2025. Pol J Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40321709 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics predicting immunohistochemical markers in primary hepatic carcinoma: Current status and challenges.Heliyon. 2024 Nov 20;10(23):e40588. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40588. eCollection 2024 Dec 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39660185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imaging-Based Prediction of Ki-67 Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Retrospective Study.Cancer Med. 2025 Feb;14(4):e70562. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70562. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 39964132 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Ki-67 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma with machine learning models based on intratumoral and peritumoral radiomic features.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025 May 15;17(5):104172. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.104172. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40487953 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence in abdominal and pelvic ultrasound imaging: current applications.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025 Apr;50(4):1775-1789. doi: 10.1007/s00261-024-04640-x. Epub 2024 Nov 2. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025. PMID: 39487919 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wei W, Jian P-E, Li S-H, Guo Z-X, Zhang Y-F, Ling Y-H, et al. . Adjuvant transcatheter arterial chemoembolization after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma patients with solitary tumor and microvascular invasion: a randomized clinical trial of efficacy and safety. Cancer Commun (Lond) (2018) 38(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s40880-018-0331-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

