Neuroprotection by upregulation of the major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC I) in SOD1G93A mice
- PMID: 37711512
- PMCID: PMC10498468
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1211486
Neuroprotection by upregulation of the major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC I) in SOD1G93A mice
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Neuroprotection by upregulation of the major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC I) in SOD1G93A mice.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Sep 23;18:1493884. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1493884. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39376212 Free PMC article.
Abstract
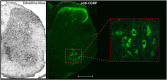
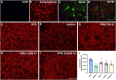
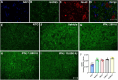
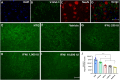
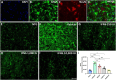
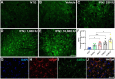
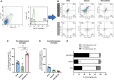
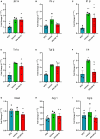
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative disease that progressively affects motoneurons, causing muscle atrophy and evolving to death. Astrocytes inhibit the expression of MHC-I by neurons, contributing to a degenerative outcome. The present study verified the influence of interferon β (IFN β) treatment, a proinflammatory cytokine that upregulates MHC-I expression, in SOD1G93A transgenic mice. For that, 17 days old presymptomatic female mice were subjected to subcutaneous application of IFN β (250, 1,000, and 10,000 IU) every other day for 20 days. Rotarod motor test, clinical score, and body weight assessment were conducted every third day throughout the treatment period. No significant intergroup variations were observed in such parameters during the pre-symptomatic phase. All mice were then euthanized, and the spinal cords collected for comparative analysis of motoneuron survival, reactive gliosis, synapse coverage, microglia morphology classification, cytokine analysis by flow cytometry, and RT-qPCR quantification of gene transcripts. Additionally, mice underwent Rotarod motor assessment, weight monitoring, and neurological scoring. The results show that IFN β treatment led to an increase in the expression of MHC-I, which, even at the lowest dose (250 IU), resulted in a significant increase in neuronal survival in the ALS presymptomatic period which lasted until the onset of the disease. The treatment also influenced synaptic preservation by decreasing excitatory inputs and upregulating the expression of AMPA receptors by astrocytes. Microglial reactivity quantified by the integrated density of pixels did not decrease with treatment but showed a less activated morphology, coupled with polarization to an M1 profile. Disease progression upregulated gene transcripts for pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, and IFN β treatment significantly decreased mRNA expression for IL4. Overall, the present results demonstrate that a low dosage of IFN β shows therapeutic potential by increasing MHC-I expression, resulting in neuroprotection and immunomodulation.
Keywords: ALS therapy; IFN β; MHC-I; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; gliosis; neuroprotection.
Copyright © 2023 Tomiyama, Cartarozzi, de Oliveira Coser, Chiarotto and Oliveira.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Delayed onset, immunomodulation, and lifespan improvement of SOD1G93A mice after intravenous injection of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue.Brain Res Bull. 2022 Aug;186:153-164. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2022.06.008. Epub 2022 Jun 17. Brain Res Bull. 2022. PMID: 35718222
-
The role of mutated SOD1 gene in synaptic stripping and MHC class I expression following nerve axotomy in ALS murine model.Eur J Histochem. 2018 May 17;62(2):2904. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2018.2904. Eur J Histochem. 2018. PMID: 29943955 Free PMC article.
-
Ablation of P2X7 receptor exacerbates gliosis and motoneuron death in the SOD1-G93A mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Oct 15;22(20):4102-16. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt259. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23736299
-
Actions of the antihistaminergic clemastine on presymptomatic SOD1-G93A mice ameliorate ALS disease progression.J Neuroinflammation. 2016 Aug 22;13(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0658-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2016. PMID: 27549088 Free PMC article.
-
Trehalose decreases mutant SOD1 expression and alleviates motor deficiency in early but not end-stage amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in a SOD1-G93A mouse model.Neuroscience. 2015 Jul 9;298:12-25. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.03.061. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 25841320
Cited by
-
Novel insights into RAGE signaling pathways during the progression of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in RAGE-deficient SOD1 G93A mice.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 8;19(3):e0299567. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299567. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38457412 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulation by 4-Hydroxy-TEMPO (TEMPOL) and Dimethyl Fumarate (DMF) After Ventral Root Crush (VRC) in C57BL/6J Mice: A Flow Cytometry Analysis.Biology (Basel). 2025 Apr 25;14(5):473. doi: 10.3390/biology14050473. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427663 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloid antigen-presenting cells in neurodegenerative diseases: a focus on classical and non-classical MHC molecules.Front Neurosci. 2024 Dec 9;18:1488382. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1488382. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39720231 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abercrombie M., Johnson M. (1946). Quantitative histology of Wallerian degeneration; nuclear population in rabbit sciatic nerve. J. Anat. 80 37–50. - PubMed
-
- Andersson M., Khademi M., Wallström E., Olsson T. (2011). Cytokine profile in interferon-ß treated multiple sclerosis patients: Reduction of interleukin-10 mRNA expressing cells in peripheral blood. Eur. J. Neurol. 4 567–571.
-
- Antonella Gasbarri A. (2014). “Involvement of glutamate in learning and memory,” in Identification of neural markers accompanying memory, ed. Meneses A. (Amsterdam: Elsevier; ).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

