Identification of Fusarium Basal Rot Pathogens of Onion and Evaluation of Fungicides against the Pathogens
- PMID: 37711982
- PMCID: PMC10498799
- DOI: 10.1080/12298093.2023.2243759
Identification of Fusarium Basal Rot Pathogens of Onion and Evaluation of Fungicides against the Pathogens
Abstract
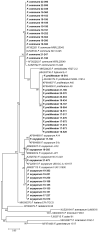
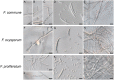
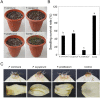
Onion (Allium cepa L.) is an economically important vegetable crop worldwide. However, various fungal diseases, including Fusarium basal rot (FBR), neck rot, and white rot, reduce onion production or bulb storage life. FBR caused by Fusarium species is among the most destructive onion diseases. In this study, we identified Fusarium species associated with FBR in Jeolla and Gyeongsang Provinces in South Korea and evaluated fungicides against the pathogens. Our morphological and molecular analyses showed that FBR in onions is associated with Fusarium commune, Fusarium oxysporum, and Fusarium proliferatum. We selected seven fungicides (fludioxonil, hexaconazole, mandestrobin, penthiopyrad, prochloraz-manganese, pydiflumetofen, and tebuconazole) and evaluated their inhibitory effects on mycelial growth of the pathogens at three different concentrations (0.01, 0.1, and 1 mg/mL). We found that prochloraz-manganese was highly effective, inhibiting 100% of the mycelial growth of the pathogens at all concentrations, followed by tebuconazole. Fludioxonil showed < 50% inhibition at 1 mg/mL for the tested isolates.
Keywords: Chemical control; Fusarium basal rot; fungicide; onion; pathogenicity.
© 2023 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group on behalf of the Korean Society of Mycology.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


References
-
- Sengupta A, Ghosh S, Bhattacharjee S.. Allium vegetables in cancer prevention: an overview. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2004;5:237–245. - PubMed
-
- Shabir I, Pandey VK, Dar AH, et al. . Nutritional profile, phytochemical compounds, biological activities, and utilisation of onion peel for food applications: a review. Sustainability. 2022;14(19):11958. doi: 10.3390/su141911958. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
