Lifestyle management of hypertension: International Society of Hypertension position paper endorsed by the World Hypertension League and European Society of Hypertension
- PMID: 37712135
- PMCID: PMC10713007
- DOI: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003563
Lifestyle management of hypertension: International Society of Hypertension position paper endorsed by the World Hypertension League and European Society of Hypertension
Abstract
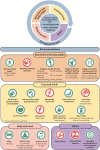
Hypertension, defined as persistently elevated systolic blood pressure (SBP) >140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) at least 90 mmHg (International Society of Hypertension guidelines), affects over 1.5 billion people worldwide. Hypertension is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) events (e.g. coronary heart disease, heart failure and stroke) and death. An international panel of experts convened by the International Society of Hypertension College of Experts compiled lifestyle management recommendations as first-line strategy to prevent and control hypertension in adulthood. We also recommend that lifestyle changes be continued even when blood pressure-lowering medications are prescribed. Specific recommendations based on literature evidence are summarized with advice to start these measures early in life, including maintaining a healthy body weight, increased levels of different types of physical activity, healthy eating and drinking, avoidance and cessation of smoking and alcohol use, management of stress and sleep levels. We also discuss the relevance of specific approaches including consumption of sodium, potassium, sugar, fibre, coffee, tea, intermittent fasting as well as integrated strategies to implement these recommendations using, for example, behaviour change-related technologies and digital tools.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
L.V. reports employment with Amsterdam University Medical Centers; consultancy agreements with AstraZeneca, Bayer BV Netherlands, Boehringer Ingelheim and Vifor Pharma; research funding from Dutch Kidney Foundation and Health Holland. Y.C.C. has received, on behalf of the Malaysian Society for World Action on Salt, Sugar and Health (MyWASSH), an unrestricted educational grant from Medtronic.
Figures
References
-
- Tomaszewski M, Itoh H. ISH2022KYOTO Hypertension Zero Declaration. Hypertens Res 2023; 46:1–2. - PubMed
-
- Cheema KM, Dicks E, Pearson J, Samani NJ. Long-term trends in the epidemiology of cardiovascular diseases in the UK: insights from the British Heart Foundation statistical compendium. Cardiovasc Res 2022; 118:2267–2280. - PubMed
-
- Elijovich F, Weinberger MH, Anderson CA, Appel LJ, Bursztyn M, Cook NR, et al. . American Heart Association Professional and Public Education Committee of the Council on Hypertension; Council on Functional Genomics and Translational Biology; and Stroke Council. Salt sensitivity of blood pressure: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Hypertension 2016; 68:e7–e46. - PubMed
-
- Appel LJ, Brands MW, Daniels SR, Karanja N, Elmer PJ, Sacks FM, et al. . American Heart Association. Dietary approaches to prevent and treat hypertension: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Hypertension 2006; 47:296–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

