Levodopa-Carbidopa Intestinal Gel Injection for Patient with Severe Parkinson's Disease Followed by Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 37712322
- PMCID: PMC10622286
- DOI: 10.1111/os.13879
Levodopa-Carbidopa Intestinal Gel Injection for Patient with Severe Parkinson's Disease Followed by Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
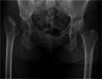
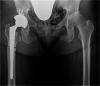
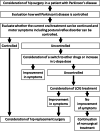
Background: Patients with Parkinson's disease have a high dislocation rate after total hip arthroplasty (THA). This study describes a case with severe Parkinson's disease who developed rapidly destructive coxarthrosis (RDC) and underwent THA using a dual mobility cup after a levodopa-carbidopa intestinal gel (LCIG) infusion.
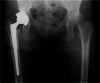
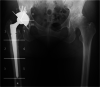
Case presentation: The patient is a 59-year-old female with a ten-year history of Parkinson's disease, which was first treated with oral levodopa. The patient developed RDC of the right hip joint. However, THA was difficult owing to Parkinson's disease and its treatment side effects, such as wearing-off, dyskinesia, and freezing of the gait, Thus, LCIG was initiated, and improvement in wearing-off and dyskinesia was observed. Two months after the LCIG therapy, the disease was controlled well. THA was subsequently performed using a dual mobility cup to prevent postoperative dislocation. Postoperatively, LCIG therapy was continuously administered to carefully manage the disease, which was controlled well with no increase in wearing-off and dyskinesia after surgery. At 1 year after surgery, the walking speed, stride length, and the Harris hip score improved compared to preoperatively. The UPDRS III motor score improved to eight without signs of wearing-off or dyskinesia. The Hoehn-Yahr scale was II in the "on" period and remained unchanged 1 year after surgery. The patient could walk without a cane and had satisfactory functional outcomes.
Conclusion: This case proved that LCIG treatment performed preoperatively, followed by THA using a dual mobility cup, and strict management of Parkinson's disease could result in a satisfactory clinical course without recurrence of wearing-off and dyskinesia. Similar procedures may benefit other patients with Parkinson's disease who have previously been deemed unsuitable for THA.
Keywords: Intestinal levodopa-carbidopa gel infusion; Parkinson's disease; Rapidly destructive coxarthrosis; Total hip arthroplasty.
© 2023 The Authors. Orthopaedic Surgery published by Tianjin Hospital and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
Figures
References
-
- Bloem BR, Okun MS, Klein C. Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 2021;397(10291):2284–2303. - PubMed
-
- Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Blankson S, Lees AJ. A clinicopathologic study of 100 cases of Parkinson's disease. Arch Neurol. 1993;50(2):140–148. - PubMed
-
- Deuschl G, Antonini A, Costa J, Śmiłowska K, Berg D, Corvol JC, et al. European academy of neurology/Movement Disorder Society‐European section guideline on the treatment of Parkinson's disease: I. Invasive Therapies Eur J Neurol. 2022;29(9):2580–2595. - PubMed
-
- Ahlskog JE, Muenter MD. Frequency of levodopa‐related dyskinesias and motor fluctuations as estimated from the cumulative literature. Mov Disord. 2001;16(3):448–458. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

