Identification of Candidate Genes that Affect the Contents of 17 Amino Acids in the Rice Grain Using a Genome-Wide Haplotype Association Study
- PMID: 37713042
- PMCID: PMC10504229
- DOI: 10.1186/s12284-023-00658-9
Identification of Candidate Genes that Affect the Contents of 17 Amino Acids in the Rice Grain Using a Genome-Wide Haplotype Association Study
Abstract
Background: The amino acid content (AAC) of the rice grain is one of the most important determinants of nutritional quality in rice. Understanding the genetic basis of grain AAC and mining favorable alleles of target genes for AAC are important for developing new cultivars with improved nutritional quality.
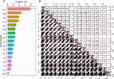
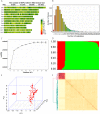
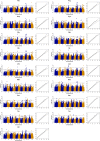
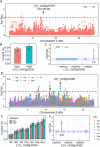
Results: Using a diverse panel of 164 accessions genotyped by 32 M SNPs derived from 3 K Rice Genome Project, we extracted 1,123,603 high quality SNPs in 44,248 genes and used them to construct haplotypes. We measured the contents of the 17 amino acids that included seven essential amino acids and 10 dispensable amino acids. Through a genome-wide haplotype association study, 261 gene-trait associations containing 174 genes for the 17 components of AAC were detected, and 34 of these genes were associated with at least two components. Furthermore, the associated SNPs in genes were also identified by a traditional genome-wide association study to identify the key natural variations in the specific genes.
Conclusions: The genome-wide haplotype association study allowed us to detected candidate genes directly and to identify key natural genetic variation as well. In the present study, twelve genes have been cloned, and 34 genes were associated with at least two components, suggesting that the genome-wide haplotype association study approach used in the current study is an efficient way to identify candidate genes for target traits. The identified candidate genes, favorable haplotypes, and key natural variations affecting AAC provide valuable resources for further functional characterization and genetic improvement of rice nutritional quality.
Keywords: Amino acid content; Candidate genes; GWAS; Genome-wide haplotype association study.
© 2023. Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification and allele mining of new candidate genes underlying rice grain weight and grain shape by genome-wide association study.BMC Genomics. 2021 Aug 6;22(1):602. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07901-x. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34362301 Free PMC article.
-
New Candidate Genes Affecting Rice Grain Appearance and Milling Quality Detected by Genome-Wide and Gene-Based Association Analyses.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Jan 4;7:1998. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01998. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28101096 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Association Analysis Dissects the Genetic Basis of the Grain Carbon and Nitrogen Contents in Milled Rice.Rice (N Y). 2019 Dec 30;12(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12284-019-0362-2. Rice (N Y). 2019. PMID: 31889226 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Basis of Variation in Rice Seed Storage Protein (Albumin, Globulin, Prolamin, and Glutelin) Content Revealed by Genome-Wide Association Analysis.Front Plant Sci. 2018 May 9;9:612. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00612. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 29868069 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding natural genetic variation for nutritional quality in grain and identification of superior haplotypes in deepwater rice genotypes of Assam, India.Gene. 2024 Nov 30;928:148801. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.148801. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Gene. 2024. PMID: 39068998
Cited by
-
Genome-wide SNPs and candidate genes underlying the genetic variations for protein and amino acids in pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum) germplasm.Planta. 2024 Jul 27;260(3):63. doi: 10.1007/s00425-024-04495-y. Planta. 2024. PMID: 39068266 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Amino Acid Profiling and 4D-DIA Proteomics Reveal Protein Quality Divergence and Metabolic Adaptation in Cordyceps Species.J Fungi (Basel). 2025 May 8;11(5):365. doi: 10.3390/jof11050365. J Fungi (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40422699 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen P, Shen Z, Ming L, Li Y, Dan W, Lou G, Peng B, Wu B, Li Y, Zhao D, Gao G, Zhang Q, Xiao J, Li X, Wang G, He Y. Genetic basis of variation in rice seed storage protein (albumin, globulin, prolamin, and glutelin) content revealed by genome-wide association analysis. Front Plant Sci. 2018;9:612. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00612. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

