Transdiagnostic risk of mental disorders in offspring of affected parents: a meta-analysis of family high-risk and registry studies
- PMID: 37713573
- PMCID: PMC10503921
- DOI: 10.1002/wps.21147
Transdiagnostic risk of mental disorders in offspring of affected parents: a meta-analysis of family high-risk and registry studies
Abstract
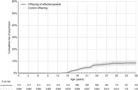
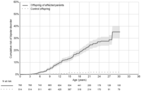
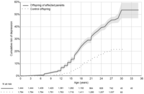
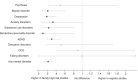
The offspring of parents with mental disorders are at increased risk for developing mental disorders themselves. The risk to offspring may extend transdiagnostically to disorders other than those present in the parents. The literature on this topic is vast but mixed. To inform targeted prevention and genetic counseling, we performed a comprehensive, PRISMA 2020-compliant meta-analysis. We systematically searched the literature published up to September 2022 to retrieve original family high-risk and registry studies reporting on the risk of mental disorders in offspring of parents with any type of mental disorder. We performed random-effects meta-analyses of the relative risk (risk ratio, RR) and absolute risk (lifetime, up to the age at assessment) of mental disorders, defined according to the ICD or DSM. Cumulative incidence by offspring age was determined using meta-analytic Kaplan-Meier curves. We measured heterogeneity with the I2 statistic, and risk of bias with the Quality In Prognosis Studies (QUIPS) tool. Sensitivity analyses addressed the impact of study design (family high-risk vs. registry) and specific vs. transdiagnostic risks. Transdiagnosticity was appraised with the TRANSD criteria. We identified 211 independent studies that reported data on 3,172,115 offspring of parents with psychotic, bipolar, depressive, disruptive, attention-deficit/hyperactivity, anxiety, substance use, eating, obsessive-compulsive, and borderline personality disorders, and 20,428,575 control offspring. The RR and lifetime risk of developing any mental disorder were 3.0 and 55% in offspring of parents with anxiety disorders; 2.6 and 17% in offspring of those with psychosis; 2.1 and 55% in offspring of those with bipolar disorder; 1.9 and 51% in offspring of those with depressive disorders; and 1.5 and 38% in offspring of those with substance use disorders. The offspring's RR and lifetime risk of developing the same mental disorder diagnosed in their parent were 8.4 and 32% for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder; 5.8 and 8% for psychosis; 5.1 and 5% for bipolar disorder; 2.8 and 9% for substance use disorders; 2.3 and 14% for depressive disorders; 2.3 and 1% for eating disorders; and 2.2 and 31% for anxiety disorders. There were 37 significant transdiagnostic associations between parental mental disorders and the RR of developing a different mental disorder in the offspring. In offspring of parents with psychosis, bipolar and depressive disorder, the risk of the same disorder onset emerged at 16, 5 and 6 years, and cumulated to 3%, 19% and 24% by age 18; and to 8%, 36% and 46% by age 28. Heterogeneity ranged from 0 to 0.98, and 96% of studies were at high risk of bias. Sensitivity analyses restricted to prospective family high-risk studies confirmed the pattern of findings with similar RR, but with greater absolute risks compared to analyses of all study types. This study demonstrates at a global, meta-analytic level that offspring of affected parents have strongly elevated RR and lifetime risk of developing any mental disorder as well as the same mental disorder diagnosed in the parent. The transdiagnostic risks suggest that offspring of parents with a range of mental disorders should be considered as candidates for targeted primary prevention.
Keywords: Familial risk; anxiety disorders; bipolar disorder; depression; eating disorders; mental disorders; psychosis; substance use disorders; targeted primary prevention; transdiagnostic risk.
© 2023 World Psychiatric Association.
Figures
References
-
- Lannes A, Bui E, Arnaud C et al. Preventive interventions in offspring of parents with mental illness: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Psychol Med 2021;51:2321‐36. - PubMed
-
- Catalan A, Salazar de Pablo G, Vaquerizo Serrano J et al. Annual Research Review: Prevention of psychosis in adolescents – systematic review and meta‐analysis of advances in detection, prognosis and intervention. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 2021;62:657‐73. - PubMed
-
- Fusar‐Poli P, Salazar de Pablo G, Correll CU et al. Prevention of psychosis: advances in detection, prognosis, and intervention. JAMA Psychiatry 2020;77:755‐65. - PubMed
-
- Loechner J, Starman K, Galuschka K et al. Preventing depression in the offspring of parents with depression: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Psychol Rev 2018;60:1‐14. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

