Risk predict model using multi-drug resistant organism infection from Neuro-ICU patients: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 37714922
- PMCID: PMC10504308
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-42522-2
Risk predict model using multi-drug resistant organism infection from Neuro-ICU patients: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
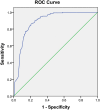
The aim of this study was to analyze the current situation and risk factors of multi-drug-resistant organism (MDRO) infection in Neuro-intensive care unit (ICU) patients, and to develop the risk predict model. The data was collected from the patients discharged from Neuro-ICU of grade-A tertiary hospital at Guizhou province from January 2018 to April 2020. Binary Logistics regression was used to analyze the data. The model was examined by receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC). The grouped data was used to verify the sensitivity and specificity of the model. A total of 297 patients were included, 131 patients infected with MDRO. The infection rate was 44.11%. The results of binary Logistics regression showed that tracheal intubation, artery blood pressure monitoring, fever, antibiotics, pneumonia were independent risk factors for MDRO infection in Neuro-ICU (P < 0.05), AUC = 0.887. The sensitivity and specificity of ROC curve was 86.3% and 76.9%. The risk prediction model had a good predictive effect on the risk of MDRO infection in Neuro ICU, which can evaluate the risk and provide reference for preventive treatment and nursing intervention.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multi-drug resistant organism infections in a medical ICU: Association to clinical features and impact upon outcome.Med Intensiva (Engl Ed). 2018 May;42(4):225-234. doi: 10.1016/j.medin.2017.07.006. Epub 2017 Oct 13. Med Intensiva (Engl Ed). 2018. PMID: 29033075 English, Spanish.
-
[Risk factors for death in elderly patients admitted to intensive care unit after elective abdominal surgery: a consecutive 5-year retrospective study].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021 Dec;33(12):1453-1458. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20210804-00118. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021. PMID: 35131012 Chinese.
-
A deep learning model for predicting multidrug-resistant organism infection in critically ill patients.J Intensive Care. 2023 Nov 9;11(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s40560-023-00695-y. J Intensive Care. 2023. PMID: 37941079 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for the effectiveness of chlorhexidine bathing and health care-associated infections among adult intensive care patients: a trial sequential meta-analysis.BMC Infect Dis. 2018 Dec 19;18(1):679. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3521-y. BMC Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30567493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibiotic heterogeneity optimizes antimicrobial prescription and enables resistant pathogen control in the intensive care unit.Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2012 Aug;13(4):194-202. doi: 10.1089/sur.2012.121. Epub 2012 Aug 22. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2012. PMID: 22913313 Review.
Cited by
-
Infection Prevention and Control Strategies According to the Type of Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria and Candida auris in Intensive Care Units: A Pragmatic Resume including Pathogens R0 and a Cost-Effectiveness Analysis.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Aug 22;13(8):789. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13080789. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39200090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distribution patterns and evolution of antimicrobial resistance in Gram-negative bacteria within the intensive care unit of a tertiary hospital from 2019 to 2024.Front Microbiol. 2025 May 15;16:1587132. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1587132. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40444004 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting infections with multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs) in neurocritical care patients with hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP): development of a novel multivariate prediction model.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Jun 3;13(6):e0246024. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02460-24. Epub 2025 May 15. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40372026 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of machine learning models to predict MDRO colonization or infection on ICU admission by using electronic health record data.Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2024 Jul 6;13(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s13756-024-01428-y. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2024. PMID: 38971777 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thoma R, et al. The challenge of preventing and containing outbreaks of multidrug-resistant organisms and Candida auris during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic: Report of a carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii outbreak and a systematic review of the literature. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2022;11:12. doi: 10.1186/s13756-022-01052-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous