A novel stepwise catheter ablation method of the mitral isthmus for persistent atrial fibrillation: efficacy and reproducibility
- PMID: 37715135
- PMCID: PMC10504774
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-023-03490-7
A novel stepwise catheter ablation method of the mitral isthmus for persistent atrial fibrillation: efficacy and reproducibility
Abstract
Background: Ethanol infusion of the vein of Marshall (EI-VOM) has been widely used to facilitate mitral isthmus (MI) ablation. According to the literature, the success rate of achieving a bidirectional conduction block across the MI ranges from 51 to 96%, with no standardized strategy or method available for cardiac electrophysiologists.
Objectives: This study aimed to introduce and evaluate a novel ablation method of MI.
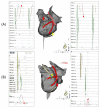
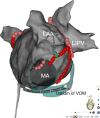
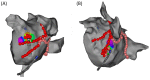
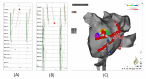
Methods: Consecutive patients with persistent atrial fibrillation (PeAF) that underwent catheter ablation were included. The MI ablation procedure followed a stepwise approach. In step 1, ethanol infusion of the vein of Marshall (EI-VOM) was performed. In step 2, a "V-shape" endocardial linear ablation connecting the left inferior pulmonary vein (LIPV) to mitral annulus (MA) was performed. In step 3, earliest activation sites(EASs) near the ablation line were identified using activation mapping followed by reinforced ablation. In step 4, precise epicardial ablation was performed, with the catheter introduced into the coronary sinus(CS) to target key ablation targets (KATs).
Results: 135 patients with PeAF underwent catheter ablation with the stepwise ablation method adopted in 119 cases. Bidirectional conduction blocks were achieved in 117 patients (98.3%). The block rates of every step were 0%, 58.0%, 44.0%, and 92.9%, and the cumulative block rates for the four steps were 0%, 58.0%, 76.5%, and 98.3%, respectively. No patient experienced fatal complications.
Conclusions: Our novel stepwise catheter ablation method for MI yielded a high bidirectional block rate with high reproducibility.
Keywords: Catheter ablation; Ethanol infusion of the vein of Marshall; Mitral isthmus ablation; Persistent atrial fibrillation.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Simplified stepwise anatomical ablation strategy for mitral isthmus: efficacy, efficiency, safety, and outcome.Europace. 2023 Feb 16;25(2):610-618. doi: 10.1093/europace/euac204. Europace. 2023. PMID: 36353823 Free PMC article.
-
Acute mitral isthmus block during catheter ablation with vein of Marshall ethanol infusion: Angiographic considerations.Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2024 Feb;117(2):119-127. doi: 10.1016/j.acvd.2023.11.001. Epub 2023 Nov 19. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2024. PMID: 38040560
-
Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation Targeting the Vein of Marshall in Difficult Mitral Isthmus Ablation or Pulmonary Vein Isolation.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2017 Apr;28(4):386-393. doi: 10.1111/jce.13161. Epub 2017 Jan 31. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2017. PMID: 28054738
-
A proposed index of myocardial staining for vein of Marshall ethanol infusion: an Italian single-center experience.J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2024 Aug;67(5):1267-1277. doi: 10.1007/s10840-023-01732-4. Epub 2024 Jan 11. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2024. PMID: 38206450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and feasibility of vein of Marshall ethanol infusion during persistent atrial fibrillation ablation: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Cardiol. 2024 Jan;47(1):e24178. doi: 10.1002/clc.24178. Epub 2023 Nov 6. Clin Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 37933170 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Acute mitral isthmus block in patients undergoing catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: efficacy and safety of a systematic stepwise approach.J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2025 May 31. doi: 10.1007/s10840-025-02074-z. Online ahead of print. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2025. PMID: 40448792
-
Morphometry of left atrial appendage isthmus and mitral isthmus: implications for atrial fibrillation catheter ablation.J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2024 Nov;67(8):1929-1942. doi: 10.1007/s10840-024-01896-7. Epub 2024 Aug 2. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2024. PMID: 39093487
References
-
- Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic surgery (EACTS): the Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2021;42(5):373–498. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa612. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kim TH, Uhm JS, Kim JY, et al. Does additional electrogram-guided ablation after linear ablation reduce recurrence after catheter ablation for longstanding persistent atrial fibrillation? A prospective randomized study. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017;6:e004811. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.004811. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

