Generation of green electricity from sludge using photo-stimulated bacterial consortium as a sustainable technology
- PMID: 37715250
- PMCID: PMC10503168
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-023-02187-y
Generation of green electricity from sludge using photo-stimulated bacterial consortium as a sustainable technology
Abstract
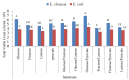
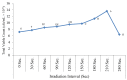
Microbial fuel cell (MFC) is a bio-electrical energy generator that uses respiring microbes to transform organic matter present in sludge into electrical energy. The primary goal of this work was to introduce a new approach to the green electricity generation technology. In this context a total of 6 bacterial isolates were recovered from sludge samples collected from El-Sheikh Zayed water purification plant, Egypt, and screened for their electrogenic potential. The most promising isolates were identified according to 16S rRNA sequencing as Escherichia coli and Enterobacter cloacae, promising results were achieved on using them in consortium at optimized values of pH (7.5), temperature (30°C) and substrate (glucose/pyruvate 1%). Low level red laser (λ = 632.8nm, 8mW) was utilized to promote the electrogenic efficiency of the bacterial consortium, maximum growth was attained at 210 sec exposure interval. In an application of adding standard inoculum (107 cfu/mL) of the photo-stimulated bacterial consortium to sludge based MFC a significant increase in the output potential difference values were recorded, the electricity generation was maintained by regular supply of external substrate. These results demonstrate the future development of the dual role of MFCs in renewable energy production and sludge recycling.
Keywords: Electrogenic Bacteria; Green Electricity; Microbial Fuel Cell (MFC); Sludge; Temperature; pH; photo-stimulation.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Microbial community composition and electricity generation in cattle manure slurry treatment using microbial fuel cells: effects of inoculum addition.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017 Oct;24(29):23226-23235. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9959-4. Epub 2017 Aug 22. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28831702
-
Conversion of activated-sludge reactors to microbial fuel cells for wastewater treatment coupled to electricity generation.J Biosci Bioeng. 2014 Nov;118(5):533-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2014.04.009. Epub 2014 May 21. J Biosci Bioeng. 2014. PMID: 24856588
-
Two-stage pretreatment of excess sludge for electricity generation in microbial fuel cell.Environ Technol. 2019 Apr;40(11):1349-1358. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2017.1422548. Epub 2018 Jan 12. Environ Technol. 2019. PMID: 29281942
-
Ceramic-microbial fuel cell (C-MFC) for waste water treatment: A mini review.Environ Res. 2022 Jul;210:112963. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.112963. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Environ Res. 2022. PMID: 35217013 Review.
-
Bioelectrochemical systems: Sustainable bio-energy powerhouses.Biosens Bioelectron. 2019 Oct 1;142:111576. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2019.111576. Epub 2019 Aug 7. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019. PMID: 31412313 Review.
References
-
- Lu N, Zhou S, Zhuang L, Zhang J, Ni J. Electricity generation from starch processing wastewater using microbial fuel cell technology. Biochem Eng J. 2009;43:246–51. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2008.10.005. - DOI
-
- Wang J, Deng H, Wu SS, Deng YC, Liu L, Han C, Jiang YB, Zhong WH. Assessment of abundance and diversity of exo-electrogenic bacteria in soil under different land use types. CATENA. 2019;172:572–80. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2018.09.028. - DOI
-
- Chakraborty I, Bhowmick GD, Nath D, et al. Removal of sodium dodecyl sulphate from wastewater and its effect on anodic biofilm and performance of microbial fuel cell. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad. 2021;156:105. doi: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2020.105108. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

