Systematic Literature Review of Real-World Evidence on Baricitinib for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 37715917
- PMCID: PMC10654279
- DOI: 10.1007/s40744-023-00591-9
Systematic Literature Review of Real-World Evidence on Baricitinib for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
Introduction: Baricitinib, an orally available small-molecule inhibitor of Janus kinase (JAK)1 and JAK2, is indicated to treat active moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Objective: This systematic review described the real-world clinical characteristics of baricitinib-treated patients with RA, prescription patterns, effectiveness, drug persistence, patient-reported outcomes (PROs; physical function, pain, health-related quality of life [HRQoL]), patient global assessment (PGA), and safety of baricitinib.
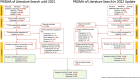
Methods: A PRISMA systematic review of real-world studies was conducted to identify relevant literature published between January 2016 and September 2022 using MEDLINE®, EMBASE®, and evidence-based medicine review databases. Websites or online repositories of the American College of Rheumatology and the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology were searched manually to include relevant abstracts from conferences held between January 2016 and November 2022.
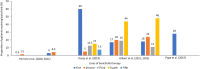
Results: A total of 11,472 records were identified by searching online databases. Seventy studies were included in the study, of which 40 were abstracts. Most patients were older (51-71 years), female, and with mean RA duration of 4-19 years. Baricitinib was mostly used after the failure of one or more bDMARDs, and 4 mg dosing was prevalent in patients with RA (range 22-100%). Clinical effectiveness of baricitinib was reported in real-world settings regardless of prior biologic/targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) use and concomitant conventional synthetic DMARD use. Achievement of Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) remission was reported in 8.7-60% of patients at week 12 and CDAI low disease activity (LDA) in 20.2-81.6% at week 24. The proportion of patients attaining Simple Disease Activity Index (SDAI) remission was reported in 12% at week 4 to 45.4% at 24 weeks. Drug persistence was high, similar, or equal to anti-tumor necrosis factor drugs. No new safety signals were identified.
Conclusion: Baricitinib demonstrated effectiveness in the real-world setting with a consistent safety profile observed in clinical studies. Better persistence rates for baricitinib compared to bDMARDs with improvement in PROs were reported, although baricitinib-treated patients had RA with poor prognostic characteristics.
Keywords: Baricitinib; Janus kinase inhibitors; Real-world evidence; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Tamas Treuer: Tamas Treuer is an employee and shareholder of Eli Lilly and Company. Ewa Haladyj: Ewa Haladyj is an employee and shareholder of Eli Lilly and Company. Jens Gerwien: Jens Gerwien is an employee and shareholder of Eli Lilly and Company. Chandreyee Dutta Gupta: Chandreyee Dutta Gupta is an employee and shareholder of Eli Lilly and Company. Blanca Hernández-Cruz: Grant and research support and consultancy fees in the last 3 years from AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Eli Lilly, Fresenius, Grunnenta, STAD, and Gilead. Uta Kiltz: Grant and research support and consultancy fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Biocad, Biogen, BMS, Chugai, Eli Lilly, Fresenius, Gilead, Grünenthal, GSK, Hexal, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, onkowoessen.de, Pfizer, Roche, UCB, and Viatris.. Jérôme Avouac: Honoraria from Pfizer, Lilly, Bristol Myers Squibb, UCB, Roche, Nordic Pharma, Novartis, Sanofi, Boehringer, AbbVie, Chugai, Galapagos, Biogen, Fresenius Kabi, Sandoz, and AstraZeneca. Research grants: Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Fresenius Kabi, Novartis, Nordic Pharma, Galapagos. Fabrizio Conti: Speaker fee: Eli Lilly, Biogen, BMS, Galapagos, AbbVie, Pfizer, UCB.
Figures

References
-
- Sung YK, Lee YH. Comparative effectiveness and safety of non-tumour necrosis factor biologics and Janus kinase inhibitors in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis showing insufficient response to tumour necrosis factor inhibitors: a Bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2021;46(4):984–992. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13380. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fleischmann R, Pangan AL, Song IH, Mysler E, Bessette L, Peterfy C, et al. Upadacitinib versus placebo or adalimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate: results of a phase III, double-blind randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(11):1788–1800. doi: 10.1002/art.41032. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

