Molecular detection of Sodalis glossinidius, Spiroplasma species and Wolbachia endosymbionts in wild population of tsetse flies collected in Cameroon, Chad and Nigeria
- PMID: 37716961
- PMCID: PMC10504758
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-023-03005-6
Molecular detection of Sodalis glossinidius, Spiroplasma species and Wolbachia endosymbionts in wild population of tsetse flies collected in Cameroon, Chad and Nigeria
Abstract
Background: Tsetse flies are cyclical vectors of African trypanosomiasis (AT). The flies have established symbiotic associations with different bacteria that influence certain aspects of their physiology. Vector competence of tsetse flies for different trypanosome species is highly variable and is suggested to be affected by bacterial endosymbionts amongst other factors. Symbiotic interactions may provide an avenue for AT control. The current study provided prevalence of three tsetse symbionts in Glossina species from Cameroon, Chad and Nigeria.
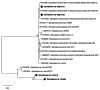
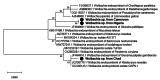
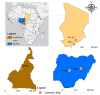
Results: Tsetse flies were collected and dissected from five different locations. DNA was extracted and polymerase chain reaction used to detect presence of Sodalis glossinidius, Spiroplasma species and Wolbachia endosymbionts, using species specific primers. A total of 848 tsetse samples were analysed: Glossina morsitans submorsitans (47.52%), Glossina palpalis palpalis (37.26%), Glossina fuscipes fuscipes (9.08%) and Glossina tachinoides (6.13%). Only 95 (11.20%) were infected with at least one of the three symbionts. Among infected flies, six (6.31%) had Wolbachia and Spiroplasma mixed infection. The overall symbiont prevalence was 0.88, 3.66 and 11.00% respectively, for Sodalis glossinidius, Spiroplasma species and Wolbachia endosymbionts. Prevalence varied between countries and tsetse fly species. Neither Spiroplasma species nor S. glossinidius were detected in samples from Cameroon and Nigeria respectively.
Conclusion: The present study revealed, for the first time, presence of Spiroplasma species infections in tsetse fly populations in Chad and Nigeria. These findings provide useful information on repertoire of bacterial flora of tsetse flies and incite more investigations to understand their implication in the vector competence of tsetse flies.
Keywords: Cameroon; Chad; Nigeria; Sodalis glossinidius; Spiroplasma species; Symbionts; Tsetse flies; Wolbachia.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Update of
-
Molecular detection of Sodalis glossinidius, Spiroplasma and Wolbachia endosymbionts in wild population of tsetse flies collected in Cameroon, Chad and Nigeria.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 May 11:rs.3.rs-2902767. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2902767/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: BMC Microbiol. 2023 Sep 16;23(1):260. doi: 10.1186/s12866-023-03005-6. PMID: 37214831 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- WHO. Trypanosomiasis, human African (sleeping sickness) [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2021 Aug 9]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/trypanosomiasis-human-a....
-
- Gibson W. Resolution of the species problem in African trypanosomes. Int J Parasitol. 2007;37(8–9):829–38. - PubMed
-
- Adams ER, Hamilton PB, Gibson WC. African trypanosomes: celebrating diversity. Trends Parasitol. 2010;26(7):324–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

