Implementation of large-scale pooled testing to increase rapid molecular diagnostic test coverage for tuberculosis: a retrospective evaluation
- PMID: 37717043
- PMCID: PMC10505184
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-41904-w
Implementation of large-scale pooled testing to increase rapid molecular diagnostic test coverage for tuberculosis: a retrospective evaluation
Abstract
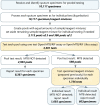
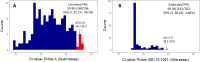
In 2021, only 6.4 million of the 10.6 million people with tuberculosis (TB) were diagnosed and treated for the disease. Although the World Health Organization recommends initial diagnostic testing using a rapid sensitive molecular assay, only 38% of people diagnosed with TB benefited from these, due to barriers including the high cost of available assays. Pooled testing has been used as an approach to increase testing efficiency in many resource-constrained situations, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, but it has not yet been widely adopted for TB diagnostic testing. Here we report a retrospective analysis of routine pooled testing of 10,117 sputum specimens using the Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra assays that was performed from July 2020 to February 2022. Pooled testing saved 48% of assays and enabled rapid molecular testing for 4156 additional people as compared to individual testing, with 6.6% of specimens positive for TB. From an in silico analysis, the positive percent agreement of pooled testing in pools of 3 as compared with individual testing for the Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra assay was estimated as 99.4% (95% CI, 96.6% to 100%). These results support the scale-up of pooled testing for efficient TB diagnosis.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The New Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra: Improving Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Resistance to Rifampin in an Assay Suitable for Point-of-Care Testing.mBio. 2017 Aug 29;8(4):e00812-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00812-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 28851844 Free PMC article.
-
Retrospective Diagnostic Accuracy Study of Abbott RealTime MTB against Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra and Xpert MTB/RIF for the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis and Susceptibility to Rifampin and Isoniazid Treatment.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Sep 3;9(1):e0013221. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00132-21. Epub 2021 Aug 18. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34406811 Free PMC article.
-
Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert Ultra assays for screening for pulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in adults, irrespective of signs or symptoms.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 23;3(3):CD013694. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013694.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33755189 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Review of Pooling Sputum as an Efficient Method for Xpert MTB/RIF Tuberculosis Testing during the COVID-19 Pandemic.Emerg Infect Dis. 2021 Mar;27(3):719-727. doi: 10.3201/eid2703.204090. Emerg Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33622482 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra performance for pulmonary tuberculosis diagnosis on smear-negative respiratory samples in a French centre.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019 Mar;38(3):601-605. doi: 10.1007/s10096-018-03463-1. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30680567
Cited by
-
Implementation of pooled testing to increase access to routine viral load monitoring for people living with HIV on antiretroviral therapy.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 27;15(1):14713. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-92709-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40289156 Free PMC article.
-
Using sputum and tongue swab specimens for in-home point-of-care targeted universal testing for tuberculosis of household contacts: an acceptability and feasibility analysis.BMJ Glob Health. 2025 Aug 21;10(8):e018131. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2024-018131. BMJ Glob Health. 2025. PMID: 40840972 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding molecular diagnostic coverage for tuberculosis by combining computer-aided chest radiography and sputum specimen pooling: a modeling study from four high-burden countries.BMC Glob Public Health. 2024;2(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s44263-024-00081-2. Epub 2024 Aug 1. BMC Glob Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39100507 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis in HIV-Positive and Diabetic Patients in Sinaloa, Mexico: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2024 Apr 22;9(4):89. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed9040089. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38668550 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the Effective Sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 Sample Pooling Based on a Large-Scale Screening Experience: Retrospective Analysis.JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024 Sep 24;10:e54503. doi: 10.2196/54503. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024. PMID: 39316785 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dorfman R. The detection of defective members of large populations. Ann. Math. Stat. 1943;14:436–440. doi: 10.1214/aoms/1177731363. - DOI
-
- Du, D.-Z. & Hwang, F. K. Combinatorial Group Testing and Its Applications, Vol. 12 (World Scientific, 1999). 10.1142/4252
-
- Bilder, C. R. Group Testing for Identification. Wiley StatsRef Stat. Ref. Online 1–11. 10.1002/9781118445112.stat08227 (2019).
-
- Hughes-Oliver, J. M. Pooling experiments for blood screening and drug discovery. In Screening 48–68. 10.1007/0-387-28014-6_3 (Springer, New York, 2006).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

