Exploring the Potential of Nanogels: From Drug Carriers to Radiopharmaceutical Agents
- PMID: 37717209
- PMCID: PMC11468994
- DOI: 10.1002/adhm.202301404
Exploring the Potential of Nanogels: From Drug Carriers to Radiopharmaceutical Agents
Abstract
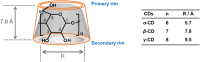
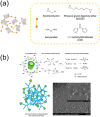
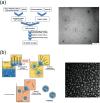
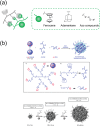
Nanogels open up access to a wide range of applications and offer among others hopeful approaches for use in the field of biomedicine. This review provides a brief overview of current developments of nanogels in general, particularly in the fields of drug delivery, therapeutic applications, tissue engineering, and sensor systems. Specifically, cyclodextrin (CD)-based nanogels are important because they have exceptional complexation properties and are highly biocompatible. Nanogels as a whole and CD-based nanogels in particular can be customized in a wide range of sizes and equipped with a desired surface charge as well as containing additional molecules inside and outside, such as dyes, solubility-mediating groups or even biological vector molecules for pharmaceutical targeting. Currently, biological investigations are mainly carried out in vitro, but more and more in vivo applications are gaining importance. Modern molecular imaging methods are increasingly being used for the latter. Due to an extremely high sensitivity and the possibility of obtaining quantitative data on pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties, nuclear methods such as single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET) using radiolabeled compounds are particularly suitable here. The use of radiolabeled nanogels for imaging, but also for therapy, is being discussed.
Keywords: cyclodextrin; drug delivery; molecular imaging; nanogels; radiolabeling; theranostics.
© 2023 The Authors. Advanced Healthcare Materials published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Advances in the development of cyclodextrin-based nanogels/microgels for biomedical applications: Drug delivery and beyond.Carbohydr Polym. 2022 Dec 1;297:120033. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.120033. Epub 2022 Aug 24. Carbohydr Polym. 2022. PMID: 36184144 Review.
-
Nanogel-based Transdermal Drug Delivery System: A Therapeutic Strategy with Under Discussed Potential.Curr Top Med Chem. 2023;23(1):44-61. doi: 10.2174/1568026622666220818112728. Curr Top Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 35984019 Review.
-
Cyclodextrin-based nanogels for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications.Int J Pharm. 2012 May 30;428(1-2):152-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2012.02.038. Epub 2012 Mar 2. Int J Pharm. 2012. PMID: 22388054 Review.
-
Chlorhexidine Loaded Cyclodextrin Containing PMMA Nanogels as Antimicrobial Coating and Delivery Systems.Macromol Biosci. 2017 Feb;17(2). doi: 10.1002/mabi.201600230. Epub 2016 Sep 20. Macromol Biosci. 2017. PMID: 27647823
-
Cyclodextrin in drug delivery: Exploring scaffolds, properties, and cutting-edge applications.Int J Pharm. 2024 Sep 5;662:124485. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.124485. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Int J Pharm. 2024. PMID: 39029633 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in Cyclodextrins and Their Derivatives in Nano-Delivery Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Aug 9;16(8):1054. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16081054. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39204399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fmoc-FF Nanogel-Mediated Delivery of Doxorubicin and Curcumin in Thyroid Cancer Cells.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Feb 17;17(2):263. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17020263. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40006633 Free PMC article.
-
Nano-chitosan hydrogel alleviates Candida albicans-induced health alterations in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): antioxidant response, neuro-behaviors, hepato-renal functions, and histopathological investigation.BMC Vet Res. 2025 Mar 8;21(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s12917-025-04568-4. BMC Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40057767 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclodextrin-Based Nanogels for Stabilization and Sensing of Curcumin.ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2024 Aug 27;7(17):20153-20162. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.4c02972. eCollection 2024 Sep 13. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2024. PMID: 39296865
-
Porous hydrogel microspheres with excellent temperature-sensitive, magnetic and fluorescent properties for drug delivery.RSC Adv. 2024 Oct 22;14(45):33449-33458. doi: 10.1039/d4ra04593a. eCollection 2024 Oct 17. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39439833 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moving forward precision medicine , Lancet 2011, 378, 1678. - PubMed
-
- National Research Council (US) Committee on A Framework for Developing a New Taxonomy of Disease . Toward Precision Medicine: Building a Knowledge Network for Biomedical Research and a New Taxonomy of Disease, National Academies Press (US), Washington (DC) 2011. - PubMed
-
- Salvati E., Stellacci F., Krol S., Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 3495. - PubMed
-
- Kojima R., Aubel D., Fussenegger M., Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2015, 28, 29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

