Global, regional, and national epidemiology of migraine and tension-type headache in youths and young adults aged 15-39 years from 1990 to 2019: findings from the global burden of disease study 2019
- PMID: 37718436
- PMCID: PMC10506184
- DOI: 10.1186/s10194-023-01659-1
Global, regional, and national epidemiology of migraine and tension-type headache in youths and young adults aged 15-39 years from 1990 to 2019: findings from the global burden of disease study 2019
Erratum in
-
Correction: Global, regional, and national epidemiology of migraine and tension-type headache in youths and young adults aged 15-39 years from 1990 to 2019: findings from the global burden of disease study 2019.J Headache Pain. 2023 Nov 22;24(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s10194-023-01693-z. J Headache Pain. 2023. PMID: 37993785 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: In recent years, headache disorders have garnered significant attention as a pressing global health issue. This concern is especially pronounced in low- to middle-income countries and exhibits a notable increase in prevalence among adolescents and young adults. Such a surge in these disorders has invariably diminished the quality of life for affected individuals. Despite its global impact, comprehensive studies exploring the ramifications of headache disorders in the younger population remain scant. Our study endeavored to quantify the global prevalence of headache disorders in individuals between the ages of 15 and 39, over a three-decade span from 1990 to 2019.
Methods: Our study, conducted from 1990 to 2019, evaluated the impact of headache disorders, specifically migraines and tension-type headaches (TTH), in 204 different countries and territories. This comprehensive assessment included a detailed analysis of incidence rates, prevalence, and disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) across various demographics such as age, gender, year, geographical location, and Socio-demographic Index (SDI).
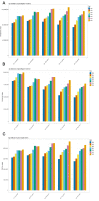
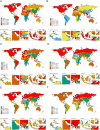
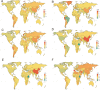
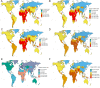
Results: In 2019, there were an estimated 581,761,847.2 migraine cases globally (95% UI: 488,309,998.1 to 696,291,713.7), marking a 16% increase from 1990. Concurrently, TTH cases numbered at 964,808,567.1 (95% UI: 809,582,531.8 to 1,155,235,337.2), reflecting a 37% rise since 1990. South Asia reported the highest migraine prevalence with 154,490,169.8 cases (95% UI: 130,296,054.6 to 182,464,065.6). High SDI regions exhibited the most substantial migraine prevalence rates both in 1990 (22,429 per 100,000 population) and 2019 (22,606 per 100,000 population). Among the five SDI classifications, the middle SDI region recorded the highest tally of TTH cases in both 1990 (210,136,691.6 cases) and 2019 (287,577,250 cases). Over the past 30 years, East Asia experienced the most pronounced surge in the number of migraine cases. On the whole, there was a discernible positive correlation between the disease burden of migraine and TTH and the SDI.
Conclusion: Migraine and TTH represent formidable challenges in global health. The intensity of their impact exhibits marked disparities across nations and is distinctly elevated among women, individuals within the 30-39 age bracket, and populations characterized by a high SDI. The results of our research emphasize the imperative of assimilating migraine and TTH management into contemporary healthcare paradigms. Such strategic integration holds the potential to amplify public cognizance regarding pertinent risk factors and the spectrum of therapeutic interventions at hand.
Keywords: Disability-adjusted life years; GBD; Global burden of disease; Migraine; SDI; Tension-type headache.
© 2023. Springer-Verlag Italia S.r.l., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests declared.
Figures
References
-
- GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators (2020) Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 396(10258):1204–22. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30925-9. Erratum in: Lancet. 2020;396(10262):1562 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

