Passive smoking and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37718995
- PMCID: PMC10501223
- DOI: 10.18332/tid/169722
Passive smoking and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Pregestational smoking increases the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and is a common health problem during pregnancy, with its incidence on the rise worldwide, especially in China. This study is a meta-analysis of passive smoking as a risk factor associated with GDM.
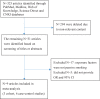
Methods: Two independent reviewers searched passive smoking and the risk of GDM in PubMed, Medline, Web of Knowledge, Science Direct, China National Knowledge Internet (CNKI) and Wanfang databases (up to May 2023). The authors extracted the study data independently and used the Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) to evaluate the quality of the included articles. A meta-analysis was conducted using a random effects model depending on the size of the heterogeneity. Begg's and Egger's tests were performed to assess publication bias.
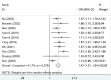
Results: The overall relative risk for GDM caused by passive smoking was 1.47 (95% CI: 1.31-1.64), with moderate heterogeneity between studies (I2=41.7%, p=0.079). Subgroup and sensitivity analyses were stable, and no evidence of publication bias was found.
Conclusions: Passive smoking is a risk factor for GDM, even in those who are not active smokers. To eliminate the effects of other confounding factors, larger prospective cohort studies are required to clarify the relationship between passive smoking and the occurrence of GDM.
Keywords: GDM; gestational diabetes mellitus; metaanalysis; passive smoking.
© 2023 Zhang H. et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have completed and submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. The authors declare that they have no competing interests, financial or otherwise, related to the current work. H. Zhang, L. Tian, J. Huang, and J. Yin report that since the initial planning of the work, this study was supported by the Shanxi Health Commission Key Laboratory of Nervous System Disease Prevention and Treatment (2020SY20) of the Sinopharm Tongmei General Hospital.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Association Between Cadmium Exposure and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Public Health. 2022 Feb 10;9:555539. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.555539. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35223753 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between TCF7L2 and CAPN10 gene polymorphisms and gestational diabetes mellitus in different geographical regions: a meta-analysis.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024 Jan 2;24(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12884-023-06177-1. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024. PMID: 38166877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A meta-analysis of passive smoking and risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015 Jan;107(1):9-14. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2014.09.019. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015. PMID: 25488377 Review.
-
A meta-analysis of active smoking and risk of meningioma.Tob Induc Dis. 2021 May 10;19:34. doi: 10.18332/tid/133704. eCollection 2021. Tob Induc Dis. 2021. PMID: 33994906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maternal height and risk of gestational diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Acta Diabetol. 2019 Jul;56(7):723-728. doi: 10.1007/s00592-019-01368-9. Epub 2019 May 20. Acta Diabetol. 2019. PMID: 31111218
Cited by
-
Secondhand smoke is associated with peptic ulcer disease and gastroesophageal reflux disease in non-smokers in a large Taiwanese population study.Front Public Health. 2024 Oct 7;12:1450481. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1450481. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39435406 Free PMC article.
-
Low Serum Levels of Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) in Immediate Postpartum Mexican Women With Gestational Diabetes.Cureus. 2025 Feb 6;17(2):e78647. doi: 10.7759/cureus.78647. eCollection 2025 Feb. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40062150 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative risk of type 2 diabetes development between women with gestational diabetes and women with impaired glucose tolerance over two decades: a multiethnic prospective cohort in New Zealand.BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2024 Dec 4;12(6):e004210. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2024-004210. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2024. PMID: 39631843 Free PMC article.
-
A retrospective evaluation of parental smoking and the risk of Type 1 diabetes in children.Tob Induc Dis. 2024 Nov 21;22. doi: 10.18332/tid/195228. eCollection 2024. Tob Induc Dis. 2024. PMID: 39575445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guan H, Shang L. Prevalence status of gestational diabetes mellitus. Article in Chinese. Chinese Journal of Practical Gynecology and Obstetrics. 2015;(1):91–94. doi: 10.7504/fk2014120120. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
