Prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis in early breast cancer patients with ultrasonic videos based deep learning
- PMID: 37719009
- PMCID: PMC10503049
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1219838
Prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis in early breast cancer patients with ultrasonic videos based deep learning
Abstract
Objective: To develop a deep learning (DL) model for predicting axillary lymph node (ALN) metastasis using dynamic ultrasound (US) videos in breast cancer patients.
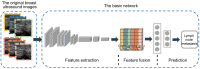
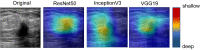
Methods: A total of 271 US videos from 271 early breast cancer patients collected from Xiang'an Hospital of Xiamen University andShantou Central Hospitabetween September 2019 and June 2021 were used as the training, validation, and internal testing set (testing set A). Additionally, an independent dataset of 49 US videos from 49 patients with breast cancer, collected from Shanghai 10th Hospital of Tongji University from July 2021 to May 2022, was used as an external testing set (testing set B). All ALN metastases were confirmed using pathological examination. Three different convolutional neural networks (CNNs) with R2 + 1D, TIN, and ResNet-3D architectures were used to build the models. The performance of the US video DL models was compared with that of US static image DL models and axillary US examination performed by ultra-sonographers. The performances of the DL models and ultra-sonographers were evaluated based on accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC). Additionally, gradient class activation mapping (Grad-CAM) technology was also used to enhance the interpretability of the models.
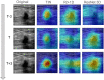
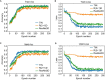
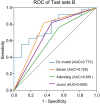
Results: Among the three US video DL models, TIN showed the best performance, achieving an AUC of 0.914 (95% CI: 0.843-0.985) in predicting ALN metastasis in testing set A. The model achieved an accuracy of 85.25% (52/61), with a sensitivity of 76.19% (16/21) and a specificity of 90.00% (36/40). The AUC of the US video DL model was superior to that of the US static image DL model (0.856, 95% CI: 0.753-0.959, P<0.05). The Grad-CAM technology confirmed the heatmap of the model, which highlighted important subregions of the keyframe for ultra-sonographers' review.
Conclusion: A feasible and improved DL model to predict ALN metastasis from breast cancer US video images was developed. The DL model in this study with reliable interpretability would provide an early diagnostic strategy for the appropriate management of axillary in the early breast cancer patients.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; axillary lymph node metastasis; breast lesion; deep learning model; ultrasound video image.
Copyright © 2023 Li, Du, Liu, Gao, Wang, Dai and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The handling editor SGW declared a shared parent affiliation with the authors W-BL, Z-CD, J-XG, QD, WH at the time of review. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Lymph Node Metastasis Prediction from Primary Breast Cancer US Images Using Deep Learning.Radiology. 2020 Jan;294(1):19-28. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2019190372. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Radiology. 2020. PMID: 31746687
-
Attention-based Deep Learning for the Preoperative Differentiation of Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Breast Cancer on DCE-MRI.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2023 Jun;57(6):1842-1853. doi: 10.1002/jmri.28464. Epub 2022 Oct 11. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36219519
-
Deep Learning Prediction of Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Breast Cancer Patients Using Clinical Implication-Applied Preprocessed CT Images.Curr Oncol. 2024 Apr 18;31(4):2278-2288. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31040169. Curr Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38668072 Free PMC article.
-
Axillary lymph node metastasis status prediction of early-stage breast cancer using convolutional neural networks.Comput Biol Med. 2021 Mar;130:104206. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.104206. Epub 2020 Dec 31. Comput Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 33421823
-
Predicting of axillary lymph node metastasis in invasive breast cancer using multiparametric MRI dataset based on CNN model.Front Oncol. 2022 Dec 6;12:1069733. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1069733. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36561533 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Use of artificial intelligence in breast surgery: a narrative review.Gland Surg. 2024 Mar 27;13(3):395-411. doi: 10.21037/gs-23-414. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Gland Surg. 2024. PMID: 38601286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrasound-based deep learning radiomics for enhanced axillary lymph node metastasis assessment: a multicenter study.Oncologist. 2025 May 8;30(5):oyaf090. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyaf090. Oncologist. 2025. PMID: 40349137 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-lesion-aware network based on freehand ultrasound video for breast cancer assessment: a prospective multicenter study.Cancer Imaging. 2025 Jun 16;25(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s40644-025-00892-y. Cancer Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40524235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allemani C, Matsuda T, Di Carlo V, Harewood R, Matz M, Nikšić M, et al. . Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival 2000-14 (CONCORD-3): analysis of individual records for 37 513 025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries. Lancet (2018) 391(10125):1023–75. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33326-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

