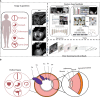
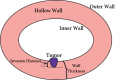
Radiomics-based T-staging of hollow organ cancers
- PMID: 37719013
- PMCID: PMC10499612
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1191519
Radiomics-based T-staging of hollow organ cancers
Abstract
Cancer growing in hollow organs has become a serious threat to human health. The accurate T-staging of hollow organ cancers is a major concern in the clinic. With the rapid development of medical imaging technologies, radiomics has become a reliable tool of T-staging. Due to similar growth characteristics of hollow organ cancers, radiomics studies of these cancers can be used as a common reference. In radiomics, feature-based and deep learning-based methods are two critical research focuses. Therefore, we review feature-based and deep learning-based T-staging methods in this paper. In conclusion, existing radiomics studies may underestimate the hollow organ wall during segmentation and the depth of invasion in staging. It is expected that this survey could provide promising directions for following research in this realm.
Keywords: T-staging; deep learning-based methods; feature-based methods; hollow organ cancer; radiomics; segmentation.
Copyright © 2023 Huang, Xu, Du, Feng, Zhang, Lu and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deep-learning-based 3D super-resolution MRI radiomics model: superior predictive performance in preoperative T-staging of rectal cancer.Eur Radiol. 2023 Jan;33(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-08952-8. Epub 2022 Jun 21. Eur Radiol. 2023. PMID: 35726100 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Machine Learning in Precision Oncology: Applications in Gastrointestinal Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 22;15(1):63. doi: 10.3390/cancers15010063. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36612061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep learning for fully automated tumor segmentation and extraction of magnetic resonance radiomics features in cervical cancer.Eur Radiol. 2020 Mar;30(3):1297-1305. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06467-3. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 31712961
-
CT-based deep learning segmentation of ovarian cancer and the stability of the extracted radiomics features.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023 Aug 1;13(8):5218-5229. doi: 10.21037/qims-22-1135. Epub 2023 Jun 13. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 37581064 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Deep Learning and Radiomics in Lung Cancer Staging: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Public Health. 2022 Jul 18;10:938113. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.938113. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35923964 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparisons among radiologist, MR findings and radiomics-clinical models in predicting placenta accreta spectrum disorders: a multicenter study.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2025 Jun;311(6):1751-1764. doi: 10.1007/s00404-025-07960-5. Epub 2025 Jan 30. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2025. PMID: 39883136 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources