Knotless barbed suture versus conventional polydioxanone suture material for intraoral surgical incisions - A randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 37719064
- PMCID: PMC10500458
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2023.08.008
Knotless barbed suture versus conventional polydioxanone suture material for intraoral surgical incisions - A randomized controlled trial
Abstract
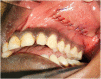
Purpose: To evaluate and compare the perioperative wound management and healing of intraoral surgical incisions between the conventional and knotless barbed Polydioxanone suture materials.
Materials and methods: A Randomized Controlled Trial was conducted with well-constructed inclusion and exclusion criteria. 46 participants were allotted into the control and test groups based on a computer-generated randomization sequence. The materials used were 3-0 Stratafix™ knotless barbed PDS suture and conventional 3-0 Ethicon PDSTMII suture materials. Parameters assessed included intraoperative time taken for closure and assessment with Early Wound Healing Score (EHS) on postoperative day 1 and Landry, Turnbull, and Howley (LTH) Healing index on postoperative days 3 and 7. Statistical analyses were done using the Chi-square test and student's t-test with a p-value less than 0.05 indicating statistical significance.
Results: 32 patients had surgical intervention for maxillofacial fracture management and 14 patient for orthognathic osteotomies. Surgical sites (n = 60) included maxillary and mandibular vestibules. Intraoperative closure time was better in the test group with statistical significance (p-value = 0.0472). The healing scores on the 3rd and 7th postoperative days were compared between the control and test groups exhibiting statistical significance favouring the test group. The p-values were 0.0479 and 0.0393 respectively.
Conclusion: To conclude, our study concurred with the existing literature in terms of reduced operating time, and better wound healing observed with the knotless barbed suture. Along with statistical significance, all the variables exhibited clinical relevance and better wound management in the test group.
Keywords: Barbed; Intraoral; Knotless; Maxillofacial; Suture.
© 2023 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Craniofacial Research Foundation.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Use of knotless barbed sutures for closure of intraoral incisions for maxillofacial trauma: a randomised controlled trial.Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2021 Feb;59(2):e72-e78. doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2020.08.015. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2021. PMID: 33384176 Clinical Trial.
-
Is There an Advantage to Knotless Barbed Suture in TKA Wound Closure? A Randomized Trial in Simultaneous Bilateral TKAs.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015 Jun;473(6):2019-27. doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4157-5. Epub 2015 Jan 29. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015. PMID: 25631171 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of Knotless Barbed Suture Versus Monofilament Suture in the Oral Cavity of Cats.J Vet Dent. 2017 Sep;34(3):148-154. doi: 10.1177/0898756417715869. Epub 2017 Jun 21. J Vet Dent. 2017. PMID: 28635369
-
A High-Strength, Absorbable, Antibacterial Knotless Tissue Control Device for Fascial Closure.Curr Obstet Gynecol Rep. 2017;6(2):175-181. doi: 10.1007/s13669-017-0208-0. Epub 2017 May 6. Curr Obstet Gynecol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28603661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Barbed vs conventional suture at cesarean delivery: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2021 Jun;100(6):1010-1018. doi: 10.1111/aogs.14080. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2021. PMID: 33404082
Cited by
-
Comparative evaluation of V-Loc knotless closure system and silk sutures in impacted mandibular third molar surgery: a split-mouth randomized controlled trial.Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2025 Aug 11;29(1):141. doi: 10.1007/s10006-025-01438-z. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2025. PMID: 40788498 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Minozzi F., Bollero P., Unfer V., Dolci A., Galli M. The sutures in dentistry. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2009;13(3):217–226. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

