Physiological response and molecular regulatory mechanism reveal a positive role of nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide applications in salt tolerance of Cyclocarya paliurus
- PMID: 37719222
- PMCID: PMC10502730
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1211162
Physiological response and molecular regulatory mechanism reveal a positive role of nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide applications in salt tolerance of Cyclocarya paliurus
Abstract
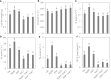
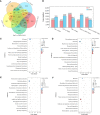
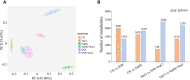
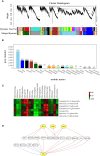
As a multifunctional tree species, Cyclocarya paliurus leaves are rich in bioactive substances with precious healthy values. To meet the huge requirement of C. paliurus leaf production, sites with some environmental stresses would be potential land for developing its plantations due to the limitation of land resources in China. Nitric oxide (NO) and hydrogen sulfide (H2S) are common gas messengers used to alleviate abiotic stress damage, whereas the mechanism of these messengers in regulating salt resistance of C. paliurus still remains unclear. We performed a comprehensive study to reveal the physiological response and molecular regulatory mechanism of C. paliurus seedlings to the application of exogenous NO and H2S under salt stress. The results showed that the application of sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS) and sodium nitroprusside (SNP) not only maintained the photosynthetic capacity and reduced the loss of leaf biomass, but also promoted endogenous NO synthesis and reduced oxidative damage by activating antioxidant enzyme activity and increasing the content of soluble protein and flavonoids. Moreover, transcriptome and metabolome analysis indicated the expression of genes encoding phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL), cytochromeP450 (CYP), chalcone synthase (CHS), dihydroflavonol 4-reductase (DFR) and flavonol synthase (FLS) in flavonoid biosynthesis pathway was all up-regulated by the application of NO and H2S. Meanwhile, 15 transcriptional factors (TFs) such as WRKY, ERF, bHLH and HY5 induced by NO were found to regulated the activities of several key enzymes in flavonoid biosynthesis pathway under salt stress, via the constructed co-expression network. Our findings revealed the underlying mechanism of NO and H2S to alleviate salt stress and regulate flavonoid biosynthesis, which provides a theoretical basis for establishing C. paliurus plantations in the salt stress areas.
Keywords: Cyclocarya paliurus; antioxidant system; exogenous substance; photosynthetic parameter; salt stress; transcription factors.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Liu, Zhang and Fang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Alamri S., Ali H. M., Khan M. I. R., Singh V. P., Siddiqui M. H. (2020). Exogenous nitric oxide requires endogenous hydrogen sulfide to induce the resilience through sulfur assimilation in tomato seedlings under hexavalent chromium toxicity. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 155, 20–34. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.07.003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Asghar T., Jamil Y., Iqbal M., Zia-ul-Haq, Abbas M. (2016). Laser light and magnetic field stimulation effect on biochemical, enzymes activities and chlorophyll contents in soybean seeds and seedlings during early growth stages. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B-Biol. 165, 283–290. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.10.022 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

