Intensive Frequent Granulocyte Adsorptive Apheresis Therapy for Acute Fulminant Ulcerative Colitis: Two Consecutive Case Reports
- PMID: 37719478
- PMCID: PMC10503873
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.43599
Intensive Frequent Granulocyte Adsorptive Apheresis Therapy for Acute Fulminant Ulcerative Colitis: Two Consecutive Case Reports
Abstract
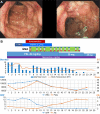
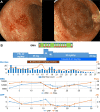
Granulocyte/monocyte adsorptive apheresis (GMA) therapy is a treatment method for ulcerative colitis (UC). Twice-weekly GMA regimens are usually administered to treat severe UC. Although GMA efficacy is considered frequency-dependent, there is no uniformly accepted optimal GMA regimen, and there is insufficient evidence regarding optimal GMA therapy frequency for acute fulminant UC. Case 1 was of a 33-year-old man, and case 2 was of a 20-year-old woman. They were diagnosed with acute fulminant UC and treated with steroid therapy, but exhibited exacerbated UC, and their conditions worsened. We, therefore, initiated intensive frequent GMA therapy (conducted 10-11 times during a 13-day period). In both cases, remission was achieved within two weeks of therapy induction. Herein, we describe two consecutive cases in which rapid remission of acute fulminant UC was achieved without adverse events using intensive frequent GMA therapy. These cases suggest that intensive frequent GMA therapy might induce rapid remission in acute fulminant UC cases and may be more effective than twice-weekly GMA regimens.
Keywords: apheresis; disease severity; granulocyte/monocyte adsorptive apheresis; intensive treatment; rapid remission; ulcerative colitis.
Copyright © 2023, Furuto et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An open-label prospective randomized multicenter study shows very rapid remission of ulcerative colitis by intensive granulocyte and monocyte adsorptive apheresis as compared with routine weekly treatment.Am J Gastroenterol. 2009 Dec;104(12):2990-5. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2009.453. Epub 2009 Sep 1. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19724269 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and Usefulness of New Single-Needle Intensive Granulocyte and Monocyte Adsorptive Apheresis in Active Ulcerative Colitis Patients Without Corticosteroids and Biologics.Ther Apher Dial. 2016 Aug;20(4):383-9. doi: 10.1111/1744-9987.12470. Ther Apher Dial. 2016. PMID: 27523079
-
Upadacitinib Plus Intensive Granulocyte and Monocyte Adsorptive Apheresis for Ulcerative Colitis Achieved Ulcer Healing for Pyoderma Gangrenosum.J Clin Med Res. 2023 Dec;15(10-11):446-455. doi: 10.14740/jocmr5005. Epub 2023 Nov 3. J Clin Med Res. 2023. PMID: 38189038 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting neutrophils in inflammatory bowel disease: revisiting the role of adsorptive granulocyte and monocyte apheresis.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Aug;16(8):721-735. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2022.2100759. Epub 2022 Jul 19. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35833363 Review.
-
Safety and clinical efficacy of granulocyte and monocyte adsorptive apheresis therapy for ulcerative colitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Jan 28;12(4):520-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i4.520. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16489663 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Factors affecting clinical and endoscopic efficacies of selective leucocytapheresis for ulcerative colitis. Yamamoto T, Saniabadi AR, Maruyama Y, Umegae S, Matsumoto K. Dig Liver Dis. 2007;39:626–633. - PubMed
-
- Adacolumn, an adsorptive carrier based granulocyte and monocyte apheresis device for the treatment of inflammatory and refractory diseases associated with leukocytes. Saniabadi AR, Hanai H, Takeuchi K, et al. Ther Apher Dial. 2003;7:48–59. - PubMed
-
- Hisamatsu group; 2023. Ulcerative colitis/Crohn’s disease diagnostic criteria/treatment guidelines revised edition. [ Aug; 2020 ]. 2023. http://www.ibdjapan.org/pdf/doc15.pdf http://www.ibdjapan.org/pdf/doc15.pdf
-
- Cyclosporine in severe ulcerative colitis refractory to steroid therapy. Lichtiger S, Present DH, Kornbluth A, et al. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:1841–1845. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
